News
-
 Climate
ClimateWarming could nearly double rate of severe La Niña events
Changing climate in the western Pacific could roughly double the frequency of severe La Niña events that cause extreme weather shifts across the globe.
-
 Anthropology
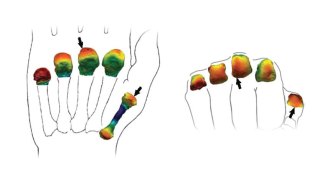
AnthropologyScans tell gripping tale of possible ancient tool use
South African fossils contain inner signs of humanlike hands, indicating possible tool use nearly 3 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceRosetta reveals a complex comet
Rosetta finds diverse landscapes on comet 67P, which could provide researchers with clues about how the solar system formed.
-
 Genetics
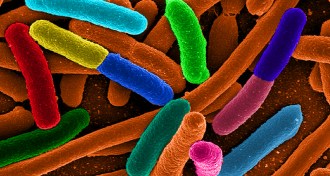
GeneticsScientists find new way to corral genetically engineered bacteria
Engineering E. coli to depend on human-made molecules may keep genetically modified bacteria from escaping into nature.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s protective barrier gets leakier with age
Aging influences the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, which may contribute to learning and memory problems later in life.
-
 Neuroscience
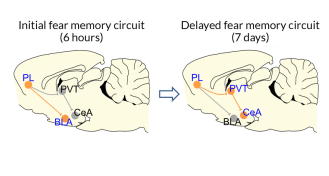
NeuroscienceNewly identified brain circuit hints at how fear memories are made
A newfound set of brain connections appears to control fear memories, a finding that may lead to a better understanding of PTSD and other anxiety disorders.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSpeed of light not so constant after all
Even in vacuum conditions, light can move slower than its maximum speed depending on the structure of its pulses.
By Andrew Grant -
 Earth
EarthFaulty thermometers exaggerated western U.S. mountain warming
Defective thermometers used in snowpack and ecology research overstated warming in western U.S. mountains.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMountain migration is a roller coaster for bar-headed geese
Bar-headed geese rise and fall to match terrain below them when migrating over the Himalayas.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyRocky planets around cool stars may have Earthlike climates
Small, rocky planets that sit close to cool stars might be able to keep spinning, creating conditions hospitable to life.
-
 Life
LifeIn battle to shape immunity, environment often beats genes
The environment, especially microbes, shapes immune system reactions more than genes do.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSquids edit genetic directions extensively
In squids, RNA editing means that DNA often does not get the final say in which proteins are created.