News
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHuman ancestors engraved abstract patterns
Indonesian Homo erectus carved zigzags on a shell at least 430,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
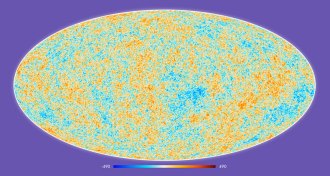 Cosmology
CosmologyMost precise snapshot of the universe unveiled
New results from the Planck satellite provide the most detailed look yet of the makeup of the universe.
-
 Life
LifeTadpole eye transplant shows new way to grow nerves
Wiring replacement organs into the body may be as easy as discharging a biological battery, new experiments with tadpoles suggest.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceComet lander’s exploration cut short
The comet lander Philae made history with its touchdown on comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, but a series of small hiccups prevented the robot from recharging its batteries, giving it only about 57 hours to explore the alien world.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTurning the immune system on cancer
A new class of drugs uncloaks tumors in some patients, awakening home-grown cells to fight several cancer types.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyGolden Fleece myth was based on real events, geologists contend
Jason’s legend grew out of long-distance trade with people who used sheepskins to collect gold.
By Bruce Bower -
 Oceans
OceansRobotic subs reveal thicker Antarctic sea ice
New measurements by robotic subs suggest that scientists have underestimated Antarctic sea ice thickness.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNegative mass might not defy Einstein
Repulsive matter could have played a role in the early universe, a computational study finds.
By Andrew Grant -
 Chemistry
ChemistryRadioactive fuel turns to goo during nuclear meltdown
Experiments reveal the atomic rearrangements that occur within uranium dioxide when nuclear reactors fail.
By Beth Mole -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBarley elevated Central Asian farmers to ‘the roof of the world’
Hardy western crops allowed villagers to settle in the cold, thin air atop the Tibetan Plateau.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBreathing returns to paralyzed rats
Scar tissue–busting enzyme plus rehabilitation therapy improves respiration long after rats’ initial spinal cord injuries.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeSprings bring gecko stickiness to human scale
Springs of a stretchy alloy let gecko-inspired adhesives work at human scales to climb glass walls or grab space junk.
By Susan Milius