News
-
 Life
LifeTibetans live high life thanks to extinct human relatives
DNA shared by modern-day Tibetans and extinct Denisovans suggests people picked up helpful genes through interbreeding with other hominids.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyTablet devices help kids with autism speak up
Talking iPads may help break the near-silence of some kids with autism.
By Bruce Bower -
 Environment
EnvironmentPlastic goes missing at sea
A survey of the world’s oceans finds far less polymer trash than expected, and researchers don’t know where the rest of the plastic is.
By Sam Lemonick -
 Life
LifeNear reefs, microbial mix dictated by coral and algae
A reef’s dominant organism, coral or algae, may determine what kind of bacteria live there.
-
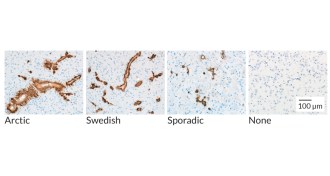 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s disease may come in distinct forms
Mouse experiments, if confirmed in people, imply that Alzheimer’s disease treatment should be personalized.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMagnetic bubbles could shield astronauts from radiation
With help from plasma and a magnet, solar storms' dangers would lessen on long space trips.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsMysterious neurotoxin may help flatworms kill prey
Tetrodotoxin, the deadly chemical in pufferfish, could help flatworms transform their earthworm prey into puddles of goo.
By Beth Mole -
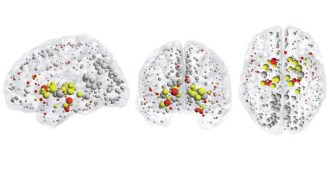 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBusy brain hubs go awry in disorders, study suggests
Schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and other brain disorders may occur when the brain’s most active hubs are damaged.
-
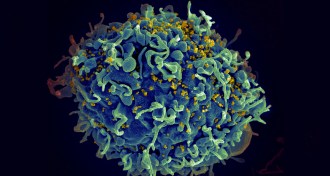 Life
LifeHIV hides in growth-promoting genes
The discovery that HIV can trigger infected cells to divide means scientists may need to rethink strategies for treating the virus that causes AIDS.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHidden heart rhythm problem may underlie some strokes
In two clinical studies, people who had had strokes with no trigger sometimes also had undiagnosed atrial fibrillation.
By Nathan Seppa -
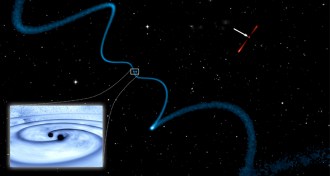 Astronomy
AstronomyRare trio of supermassive black holes found
Three supermassive black holes residing where two distant galaxies collide offer new clues about where to look for gravitational waves.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWeapon inspection scheme would test for nukes but keep designs secret
Technique borrowed from computer science could improve weapon verification and encourage countries to agree to nuclear disarmament.
By Andrew Grant