Uncategorized
-
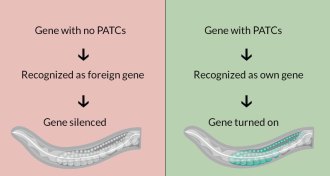
-
 Science & Society
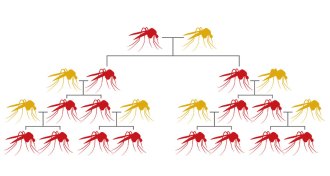
Science & SocietyGM mosquitoes succeed at reducing dengue, company says
GM mosquito releases in Brazil have helped cut dengue cases 91 percent in a year.
By Susan Milius -
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyBlack hole born without stellar parent, evidence suggests
A galaxy in the early universe might harbor the first known “direct collapse” black hole, one that forms when a cloud of gas collapses under its own weight without forming stars.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyTwo groups spread early agriculture
The Fertile Crescent was a diverse place. Multiple cultures were involved in the dawn of farming.
-
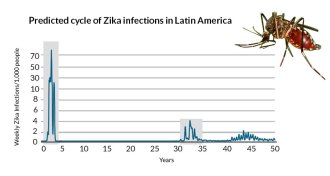 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika epidemic peaking in Latin America
Zika virus is burning through the population of Latin America; the epidemic will probably be over within two years, and won’t strike again for at least 10 years or more, a new analysis suggests.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyWhy the turtle got its shell
Fossil evidence suggests that turtles’ ancestors started to form precursors to today’s shells to help them dig, not to protect themselves.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJuno snaps its first pic of Jupiter
Jupiter and three of its moons take center stage in the first snapshot taken by the Juno spacecraft since arriving at the planet on July 4.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStill mysterious, aging may prove malleable
Our editor in chief discusses the science of aging.
By Eva Emerson -
 Life
LifeA healthy old age may trump immortality
Despite disagreements about what aging is and isn't, scientists have reached a radical consensus: It can be delayed.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe brain’s blueprint for aging is set early in life
The brain's decline may mirror its beginning, offering clues to aging.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOrganisms age in myriad ways — and some might not even bother
There is great variety in how animals and plants deteriorate (or don’t) over time.
By Susan Milius