Uncategorized
-
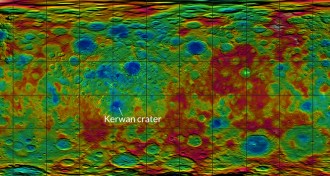 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMap of Ceres’ surface shows surprises
Clusters of craters on Ceres and smooth landscapes hint at an unusual past for the dwarf planet.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDust components may promote obesity
Fat dust bunnies may contain obesity-boosting chemicals.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateIceless Arctic summers now expected by 2050s
The Arctic Ocean will have its first ice-free summer in the 2050s, nine years earlier than previously forecast, according to improved simulations.
-
 Climate
ClimateDesert dig uncovers caches of missing CO2
Irrigation water may wash significant amounts of carbon into groundwater systems beneath Earth’s deserts, researchers propose.
-
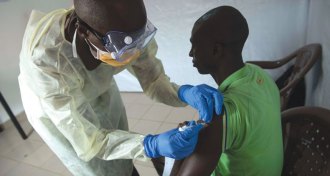 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola vaccine protects people in West Africa
In Guinea trial, zero cases of Ebola occurred in people potentially exposed who received immediate shots of a new experimental vaccine.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe five basic tastes have sixth sibling: oleogustus
Scientists dub the taste of fat oleogustus.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhere salamanders should be very afraid
Three zones of North America at high risk if the salamander-killing fungus disease Bsal invades.
By Susan Milius -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNew results from Philae lander offer first close-up of a comet
Philae’s bouncy journey across comet 67P allowed it to check out two very different sites before taking a detailed look at both the inside and outside of the comet.
-

-
 Animals
AnimalsCaterpillar treats and tricks ants by oozing spiked juice
Caterpillars ooze droplets that lure ants away from colony duties to instead lick and defend their drug source, new lab tests suggest.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsWolves in jackals’ clothing
Africa’s golden jackals are really a species of wolf and deserve a name change, DNA evidence indicates.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNew view of mouse brain provides up-close look at nerve cells’ habitat
Detailed reconstruction of a tiny fleck of mouse brain reveals neural complexity.