
Biomedical writer Aimee Cunningham is on her second tour at Science News. From 2005 to 2007, she covered chemistry, environmental science, biology and materials science for Science News. Between stints Aimee was a freelance writer for outlets such as NPR and Scientific American Mind. She has a degree in English from the University of Michigan and a master’s degree in science journalism from New York University. She received the 2019 Award for Excellence in Science and Medical Journalism from the Endocrine Society for the article "Hormone replacement makes sense for some menopausal women."

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Aimee Cunningham
-
 Health & Medicine
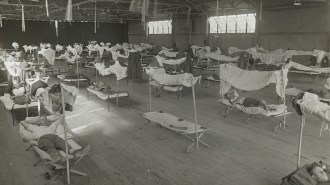
Health & MedicineEpidemics have happened before and they’ll happen again. What will we remember?
A century’s worth of science has helped us fend off infectious pathogens. But we have a lot to learn from the people who lived and died during epidemics.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA deadly fungus behind hospital outbreaks was found in nature for the first time
Learning where the fungus Candida auris thrives in nature could help reveal why this yeast is dangerous to humans.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe COVID-19 pandemic is now a year old. What have scientists learned?
As we enter the pandemic’s second year, researchers share what they’ve learned and what they look forward to.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 vaccines may be ready for teens this summer
Vaccinating children against COVID-19 is a crucial step towards reaching herd immunity and returning to pre-pandemic life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe COVID-19 death toll sent U.S. life expectancy plunging in 2020
Estimates show that American’s overall life expectancy declined by a year, but for Black Americans, the drop was almost three years.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe animals that ticks bite in the U.S. South can impact Lyme disease spread
Ticks in the north primarily attach to mice, which do a good job of infecting them with Lyme bacteria, setting up the spread to people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNearly half a million U.S. children missed out on lead tests in early 2020
A big drop in routine lead tests, which can identify children with elevated blood levels, is another troubling sign of the pandemic’s toll.
-
 Health & Medicine
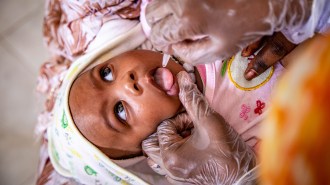
Health & MedicineA new polio vaccine joins the fight to vanquish the paralyzing disease
Work on the ground to vaccinate children continues in the push to finally eradicate polio.
-
 Health & Medicine
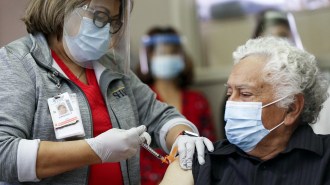
Health & MedicineSevere allergic reactions to COVID-19 vaccines are extremely rare, CDC says
Out of the first 1.9 million doses of Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine given in the United States, there were 21 reported cases of anaphylaxis, a CDC study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHealth care workers and long-term care residents should get COVID-19 vaccines first
With an initial 40 million doses of the vaccines, enough for 20 million people, anticipated by year-end, health officials are setting priorities.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLong-lasting shots work better than daily pills to prevent HIV in at-risk women
A more discreet HIV prevention method — a shot once every eight weeks —could help to boost use in women at risk.
-
 Health & Medicine
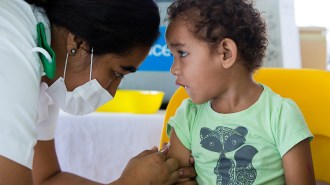
Health & MedicineMeasles has come back with a vengeance in the last several years
The steep number of measles cases in 2019 doesn’t bode well for 2020, considering disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.