Astronomy
-
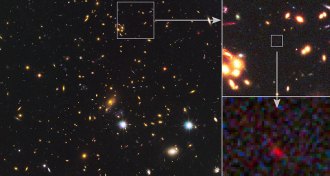 Cosmology
CosmologyThese stars may have been born only 250 million years after the Big Bang
Scientists find evidence that stars were forming just 250 million years after the universe was born.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe recipes for solar system formation are getting a rewrite
A new understanding of exoplanets and their stars is rewriting the recipes for planet formation.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyFirst 3-D map of a gas cloud in space shows it’s flat like a pancake
An interstellar gas cloud dubbed the Dark Doodad Nebula looks like a wispy, thin cylinder. But it’s actually a flat sheet.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyGaia delivers a trove of data revealing secrets of the Milky Way
Astronomers are already using Gaia’s new information to estimate the galaxy’s mass, the diameter of exoplanets and more.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNew ideas about how stars die help solve a decades-old mystery
New ideas about stellar evolution help explain why astronomers see so many bright planetary nebulae where they ought not be.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceGetting NASA’s Pluto mission off the ground took blood, sweat and years
Alan Stern talks about the new book ‘Chasing New Horizons’ and what’s next for the spacecraft that got close to Pluto.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNeutron stars shed neutrinos to cool down quickly
Scientists find the first clear evidence of rapid cooling of a neutron star by neutrino emission.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe latest star map from the Gaia spacecraft plots 1.7 billion stars
The Gaia spacecraft’s latest data release brings the number of stars with precisely measured motions up from 2 million to more than 1.3 billion.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyYoung galaxies are flat, but old ones are more blobby
A survey of hundreds of star systems precisely links the shape of a galaxy to the ages of its stars.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyCelebrity names now mark places on Pluto’s moon Charon
Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, now has 12 new names for its topological features.
By Dan Garisto -
 Astronomy
AstronomyNASA’s TESS spacecraft launches to begin its exoplanet search
After reaching its orbit in about two months, the telescope will start scanning nearby stars telltale dips in light that signal a passing planet.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyDelayed launch of NASA’s next exoplanet hunter is now set for tonight
NASA’s next exoplanet hunter, TESS, launches today to seek planets in 85 percent of the sky.