Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Earth
Earth20 years after Hurricane Katrina, is the U.S. better prepared?
Hurricane forecasts have improved since Katrina, but risks from climate change and budget cuts loom.
-
 Earth
EarthUseful metals get unearthed in U.S. mines, then they’re tossed
Recovering these metals from mining by-products destined for waste sites could offset the need to import them from elsewhere or open new mines.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Environment
EnvironmentA glacier burst, flooding Juneau. Again. This one broke records
A warming climate is behind growing floods of glacier meltwater in Alaska’s capital. Scientists say it’s the new normal.
By Douglas Fox -
 Animals
AnimalsWarm autumns could be a driver in monarch butterflies’ decline
In the lab, higher temperatures during fall migration led monarchs to break their reproductive pause, increasing their risk of death.
By Jude Coleman - Environment
See how aerosols loft through Earth’s sky
Aerosols, small particles in the atmosphere like salt and dust, may offset a third of human-caused climate warming, though their influence is fading.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Animals
AnimalsThe mystery of melting sea stars may finally be solved
A bacterium called Vibrio pectenicida may be melting sea stars along North America’s Pacific coast.
- Paleontology
A new species of ‘penis worm’ was discovered in the Grand Canyon
A trove of fossils, including a penis worm with a spiked, invertible throat, suggests this spot may have been a cradle of Cambrian evolution.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Plants
PlantsPotatoes have their roots in ancient tomatoes
Knowing potatoes’ origin story could help future-proof the crucial crop against climate threats.
-
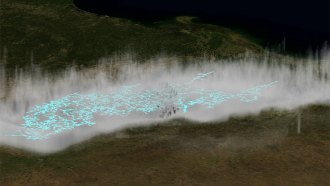 Climate
ClimateA Midwest ‘megaflash’ is the longest lightning on record
A reanalysis of satellite data shows that a 2017 Texas-to-Missouri lightning megaflash stretched 829 kilometers and lasted 7.39 seconds.
-
 Earth
EarthWhy devastating tsunamis didn’t follow the Russia earthquake
Geologists unpack why the magnitude 8.8 temblor — the sixth largest ever recorded — fomented waves that reached Japan and Hawaii but caused little damage.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Climate
ClimateWhat to know about the extreme U.S. flooding — and ways to stay safe
An oceanographer explains how climate change, warming oceans and a souped-up atmosphere are creating conditions for deadly floods.
-
 Earth
EarthHow hot can Earth get? Our planet’s climate history holds clues
Earth has survived huge temperature swings over eons of climate change. Humans might not be so lucky.
By Elise Cutts