Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDengue vaccine offers partial protection
Shots reduce severe cases of dengue among children in large study in Latin America.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIncrease in Denmark’s autism diagnoses caused by reporting changes
Changes in how autism is detected and recorded explain 60 percent of the recent increase in diagnoses, a Danish study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMoms are more likely than dads to chat with newborns
Even when fathers are around, mothers tend to talk to their babies more and respond to infants’ vocalizations.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryChemist tackles complex problems with simplicity
Harvard chemist George Whitesides applies his unique problem-solving philosophy to creating new diagnostic devices for the developing world.
By Sam Lemonick -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMini stomachs grown in lab
Clumps of human gastric cells could help researchers study stomach diseases.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHeavy milk drinking may double women’s mortality rates
In a study of 60,000 Swedes, drinking three or more classes of milk a day was associated with higher chances of death, cancer and hip fractures.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHarmless bacterium edges out intestinal germ
Researchers treated C. difficile infections in mice with a closely related bacteria that blocks C. difficile growth.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDaylight savings time tied to more exercise in children
Kids in Europe and Australia are slightly more active in longer-lit evenings, a new study shows.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCocoa antioxidants boost the aging brain
High doses of cocoa flavanols can improve some types of brain function in older individuals, a new study shows.
-
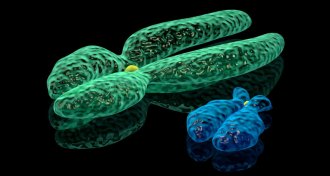 Genetics
GeneticsMen who lose Y chromosome have high risk of cancer
Losing the Y chromosome in blood cells may bring on cancer and shorten men’s lives.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThere’s no need to panic about enterovirus
The enterovirus behind this year’s outbreak, EV-D68, has been around for decades and generally causes mild symptoms.
-
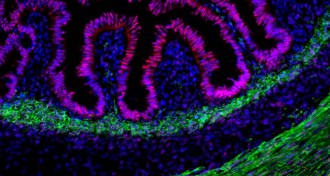 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTiny human intestine grown inside mouse
Human gut tissue transplanted into a mouse can grow into a working intestine that doctors could use to test disease treatments.
By Meghan Rosen