Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Oceans
OceansMasses of shrimp and krill may play a huge role in mixing oceans
Hoards of migrating shrimp and krill can cause large-scale turbulence in the ocean, a new study suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese seals haven’t lost their land ancestors’ hunting ways
Clawed pawlike forelimbs help true seals hunt like their land-dwelling ancestors.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA new plastic film glows to flag food contaminated with dangerous microbes
Plastic patches that glow when they touch some types of bacteria could be built into food packaging to reduce the spread of foodborne illness.
-
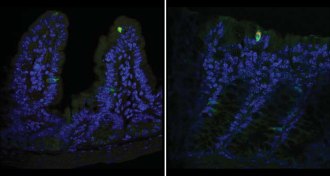 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis is how norovirus invades the body
Norovirus targets a rare type of gut cell, a study in mice finds.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSweet potatoes might have arrived in Polynesia long before humans
Genetic analysis suggests that sweet potatoes were present in Polynesia over 100,000 years ago, and didn’t need help crossing the Pacific.
By Dan Garisto -
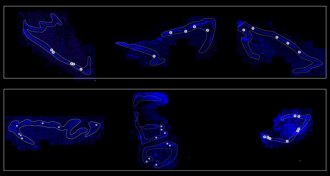
 Animals
AnimalsThese hummingbirds aim their singing tail feathers to wow mates
Acoustic cameras reveal how male Costa’s hummingbirds can aim the sound produced by fluttering tail feathers during courtship dives.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyColorful moth wings date back to the dinosaur era
Microscopic structures that scatter light to give color to the wings of modern butterflies and moths date back almost 200 million years.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThis material uses energy from ambient light to kill hospital superbugs
A quantum dot–powered material could help reduce the number of hospital-acquired infections, including those with drug-resistant bacteria.
-
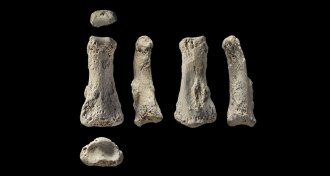 Anthropology
AnthropologyFinger fossil puts people in Arabia at least 86,000 years ago
A desert discovery suggests that Arabia was an ancient human destination.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeFossils sparked Charles Darwin’s imagination
Darwin’s Fossils recounts how finding extinct species in South America helped Charles Darwin develop his theory of evolution.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsIn a colony, king penguins behave like molecules in a 2-D liquid
Positions of king penguins in a breeding colony resemble molecules in a 2-D liquid.
By Dan Garisto -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHuman brains make new nerve cells — and lots of them — well into old age
In humans, new neurons are still born in old brains, new research suggests.