Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
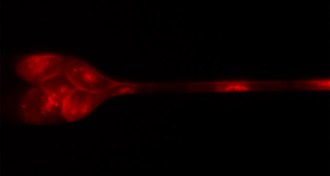
AnimalsCave-dwelling salamander comes pigmented and pale
Something’s funny in the family tree of pale, slinky cave salamanders.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
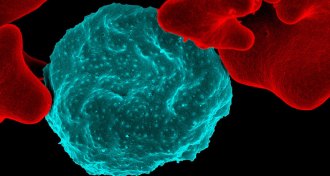
Health & MedicineClusters of cancer cells get around by moving single file
Clusters of cancer cells squeeze through thin blood vessels by aligning single file.
-
 Space
SpaceWill we know extraterrestrial life when we see it?
Desert varnish and certain minerals hint that life — here and elsewhere — may defy current criteria.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists find a crab party deep in the ocean
A trip to check out the biodiversity off the coast of Panama revealed thousands of crabs swarming on the seafloor.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘House of Lost Worlds’ opens vaults of renowned natural history museum
'House of Lost Worlds' pays homage to Yale’s Peabody Museum of Natural History and to the colorful scientists who made the museum great.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis week in Zika: Assessing risk, mosquito range, a transmission first and more
Several new reports document Zika infection in U.S. pregnant women, a case of male sexual transmission, the range of Zika-carrying mosquitoes and more.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene-edited mushroom doesn’t need regulation, USDA says
A CRISPR-edited mushroom isn’t like other GMOs, the U.S. Department of Agriculture says.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMath models predict mysterious monarch navigation
Researchers have come up with a series of equations to predict how monarchs use their eyes and antennae to figure out how to get to Mexico.
-
 Life
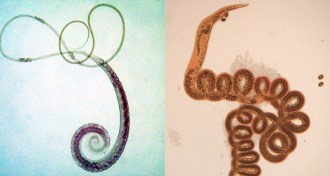
LifeHaving worms can be good for the gut
Parasitic worms shift gut microbes and protect against bowel disease.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHeat may outpace corals’ ability to cope
Corals may soon lose their ability to withstand warming waters.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMalaria parasite doesn’t pass drug immunity to its offspring
Malaria parasites resistant to the antimalarial drug atovaquone die in mosquitoes, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPied flycatchers cruise nonstop for days to cross the Sahara
Teeny, tiny passerine birds called pied flycatchers fly day and night during their annual migration south across the Sahara.