Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika’s role as a cause of severe birth defects confirmed
A new analysis from the Centers for Disease control and Prevention confirms that Zika virus infection causes microcephaly and other severe birth defects.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSpinal cord work-around reanimates paralyzed hand
A neural prosthesis can bypass a severed spinal cord, allowing a paralyzed hand to once again move.
-
 Climate
ClimatePollen becoming bee junk food as CO2 rises
Rising CO2 lowers protein content in pollen, threatening nutrition for bees.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsNew species of tumbleweed is just as bad as its parents
Two species of invasive tumbleweeds hybridized into a third. A new study finds it probably will be invasive, too.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSome people are resistant to genetic disease
People who should have genetic diseases but don’t may point to new treatments.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis week in Zika: New mouse model, virus vs. placenta, nerve insulation loss
In three new papers, scientists present a tool for studying Zika, strike down a theory of infection and offer a broad look at what the virus does to the brain.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsResearchers edit genes in human embryos for second time
Researchers in China deploy CRISPR to alter genes in human embryos again — this time to make cells HIV-resistant.
-
 Health & Medicine
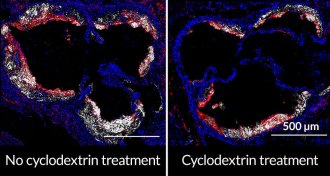
Health & MedicineA sugar can melt away cholesterol
A sugar called cyclodextrin removes cholesterol from hardened arteries in mouse studies.
-
 Climate
ClimateScience’s inconvenient (but interesting) uncertainties
In the latest issue of Science News, Editor in Chief Eva Emerson talks climate change, mouth microbes, and synthetic life.
By Eva Emerson -
 Oceans
OceansReaders question ocean health
Ocean plastics, ant behavior, pollution solutions and more in reader feedback.
-
 Animals
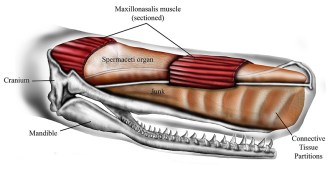
AnimalsA sperm whale’s head is built for ramming
Computer simulations of a sperm whale’s head show that an organ called the junk may help protect the brain when ramming other whales — or ships.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPiggybacking tadpoles are epic food beggars
Tadpoles beg so frantically among mimic poison frogs that researchers check to see whether they’re just scamming.
By Susan Milius