Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeNew habitat monitoring tools find hope for tigers
Free tools such Google Earth Engine and Global Forest Watch show there’s still enough forest left for tigers — if it’s protected.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsIn the Coral Triangle, clownfish figured out how to share
In the Coral Triangle in Southeast Asia, an area of rich biodiversity, clownfish species often share anemones, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLethal bat disease moves west
For the first time, the bat-killing white-nose syndrome shows up west of the Rockies.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsWhite-nose bat disease jumps the Rockies to Washington state
For the first time, the bat-killing white-nose syndrome shows up west of the Rockies.
By Susan Milius -
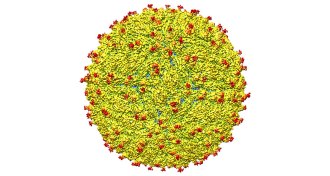 Life
LifeZika structure mapped for first time
The newly solved structure of Zika offers scientists clues on how to combat the virus.
By Meghan Rosen -
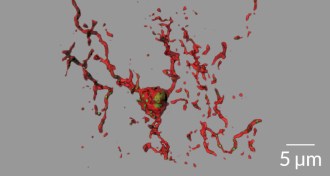 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNerve cell links severed in early stages of Alzheimer’s
Nerve cell connections may be trimmed too much in early stages of Alzheimer’s.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAncient snake wore green
Scientists have reconstructed the skin coloration of a fossilized snake that’s about 10 million years old.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGreen was this ancient snake’s signature color
Scientists have reconstructed the skin coloration of a fossilized snake that’s about 10 million years old.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient Assyrians buried their dead with turtles
Why did ancient Assyrians bury their dead with turtles? The reptiles may have served as symbolic protectors of the dead.
-
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change now bigger menace than forest loss for snowshoe hares
Shorter snow seasons push climate change ahead of direct habitat loss as menace for Wisconsin snowshoe hares.
By Susan Milius -
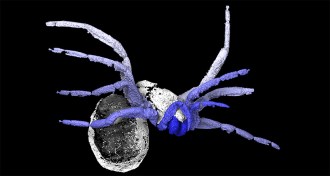 Animals
AnimalsAncient arachnid was almost a spider
A newly discovered ancient arachnid might offer clues on spider origins.
-
