Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
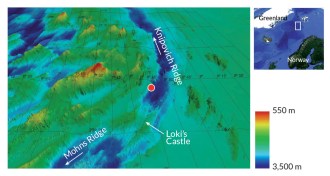 Microbes
MicrobesPossible nearest living relatives to complex life found in seafloor mud
New phylum of sea-bottom archaea microbes could be closest living relatives yet found to the eukaryote domain of complex life that includes people.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsIvory listings found on Craigslist as elephant poaching continues
Elephants are hunted by the thousands to meet demand for ivory products.
-
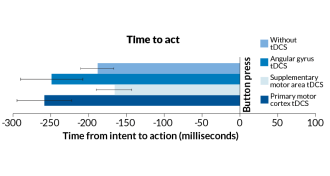 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceStimulating nerve cells stretches time between thinking, doing
A head zap can stretch the time between intention and action.
-
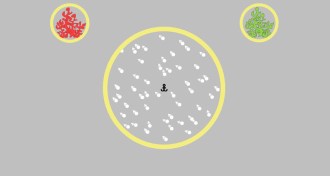 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChildren with autism excel at motion detection test
Children with autism outperform children without the disorder on a test that requires averaging the movements of lots of dots.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyOldest known avian relative of today’s birds found in China
Fossil find suggests modern birds’ oldest avian relative lived about 6 million years before previous record holder.
By Meghan Rosen -
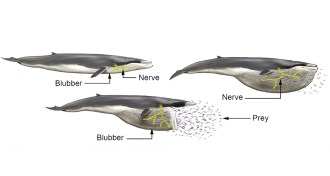 Animals
AnimalsStretchy nerves help some big whales open wide
Blue whales and their closest relatives have stretchy nerves near their mouths so they can open wide and swallow a lot of prey.
-
 Genetics
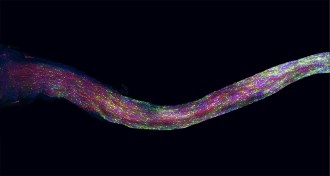
Genetics‘Brainbow’ illuminates cellular connections
A mouse’s optic nerve fluoresces in a rainbow of colors. The image offers a detailed look at nerve-protector cells called oligodendrocytes.
-
 Genetics
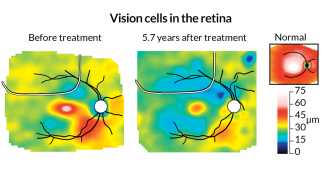
GeneticsGene therapy for blindness dims a bit
Gene therapy improves vision temporarily but can’t save sight.
-
 Neuroscience
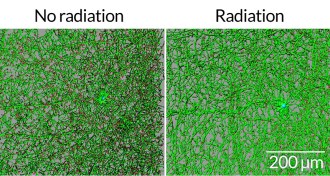
NeuroscienceZipping to Mars could badly zap brain nerve cells
Charged particles like the ones astronauts might encounter wallop the brain, mouse study suggests.
-
 Plants
PlantsHow slow plants make ridiculous seeds
Coco de mer palms scrimp, save and take not quite forever creating the world’s largest seeds.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsLazy sunfish are actually active predators
Ocean sunfish were once thought to be drifting eaters of jellyfish. But they’re not, new research shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBeetle’s toxic, explosive vapor explained
From a two-chambered gland in their rears, bombardier beetles unleash a toxic, blazing hot spray to defend themselves.
By Beth Mole