Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
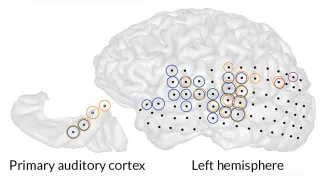
NeuroscienceTinnitus causes widespread trouble
People don’t just hear the phantom ringing of tinnitus in the part of the brain that processes sounds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCatching Zs may snag memories, too
Flies genetically destined to be forgetful could boost their memory with sleep.
-

-
 Genetics
GeneticsMosquito bites might be foretold in genes
Attractiveness to mosquitoes could be inherited, twin study suggests.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyYour toy stegosaurus may be a girl
Male and female stegosaurs may have looked different, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBees may like neonicotinoids, but some may be harmed
Two high-profile tests raise worries that bees can’t avoid neonicotinoid pesticides and that wild species are at special risk.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsOnly three wolves left on Michigan island
Without an infusion of new wolves, the Isle Royale wolf population, and the famous study associated with it, will die off.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsParticle hunting in space, life in the urban jungle and more reader feedback
Readers discuss wheat's journey to England, share stories about urban wildlife and more.
-
 Space
SpaceDriving Curiosity to discovery
Discovery is driven by curiosity, on Mars and closer to home.
By Eva Emerson -
 Animals
AnimalsGrowth of mining on land may promote invasions at sea
Ballast water taken in to keep ships stable could, when discharged elsewhere, release species that become invasive in their new homes.
-
 Life
LifeBolder snails grow stronger shells
Bold snails have tougher shells than shy snails. Understanding what drives snails to develop such differences is a bit of a challenge.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFinland’s brown bears on surprise fast track to recover diversity
Brown bears in southern Finland show surprisingly fast improvements in genetic diversity and connections with other bears.
By Susan Milius