Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: The nose knows a trillion odors
Humans can suss out more than 1 trillion different smells, a 2014 study estimated.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyYear in review: Roster of dinosaurs expands
With the discovery of several new species and a few dogma-shaking revelations, dinosaurs got a total rethink in 2014.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsYear in review: The post-pigeon century
Birds' troubles received an eerie emphasis in the news when biologists marked the 100th anniversary of the death of the last known passenger pigeon.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsYear in review: Life’s complexity recoded
New genetic letters in bacteria and a simplified yeast chromosome showcase scientists' advances in understanding the simplicity and complexity of life.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAustralia’s unexpectedly dangerous creatures
Australia is home to an array of deadly things — from crocodiles to venomous snakes — but dangers can also be found among seemingly safe critters.
-
 Ecosystems
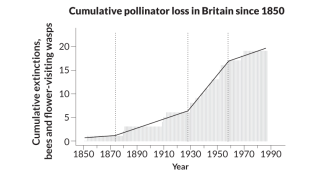
EcosystemsBee losses followed World Wars
British historical records show a century-long decline of important pollinators: bees and some wasps.
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifeNew tree of life confirms strange history of birds
A genetic analysis supports some odd groupings in the bird tree of life, showing a lot of convergent evolution in avian history.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthMega volcanism indicted in dinosaur demise
Precision dating strengthens idea that climate-altering Deccan volcanism contributed to dinosaur extinction.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGene variant linked to robust flu vaccine response
Targeting an immune signaling protein called interleukin-28B might boost protection generated by flu shots.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsEarly heart attack tied to rare mutations in two genes
Rare mutations in two genes greatly increase the risk of having a heart attack early in life, a study shows.
-
 Life
LifeImprisoning parasites can deter malaria’s spread
Disabling a protein traps malaria-causing parasites within red blood cells and prevents the organisms from reproducing.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNew type of stem cells, fuzzy and flexible
A new way to make stem cells produces fuzzy cells that appear as flexible as other types of stem cells, but are easier to grow in the lab and avoid ethical issues.