Physics
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Tech
TechSolar cell powers water-to-hydrogen conversion
High efficiency could make perovskite solar cells useful for generating environmentally friendly fuel.
By Sam Lemonick -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBanana peel slipperiness wins IgNobel prize in physics
Cartoons taught us that banana peels make for a slick trip to the floor, but scientists decided to find out just how slippery they could be.
-
 Math
MathSharks’ hunting paths may not be driven by math
Penguins, tuna, sharks and other marine hunters have been shown to use math to find food. But simulations suggest the behavior is a result of rough water, not complex calculation.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceMaking metamaterials ‘digital’ could simplify invisibility cloaks
The digital world of 1s and 0s has inspired a simpler way to make complex metamaterials.
By Andrew Grant -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsThree photons entangled, not just two
Physicists have found a way to entangle a trio of photons, but it works only once in every quadrillion attempts.
By Andrew Grant -
 Tech
TechHydrogen made using sunlight, cheap materials
Photosynthesis-inspired fuel cell uses water to make hydrogen gas and could feature in next-generation cars.
By Sam Lemonick -
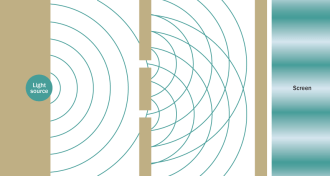 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsNew analysis rescues quantum wave-particle duality
An experiment that supposedly contradicted the wave-particle duality principle of quantum physics has been reanalyzed, revealing a flaw.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsEvidence for new Higgs-related particle fades away
A close look at data from the Large Hadron Collider finds no evidence that the Higgs boson decays into a new, unknown particle.
By Andrew Grant -
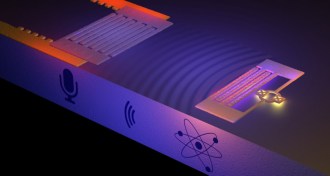 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsArtificial atom probes sound’s quantum side
Scientists have designed an artificial atom to emit sound that is divided into quantum particles.
-
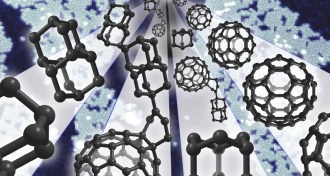 Materials Science
Materials ScienceBuckyballs, diamonds inspire new synthetic molecule
Hitching a hollow ball of carbon to a diamond-shaped lattice yields a useful piece of electrical circuitry.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsHolography entangles quantum physics with gravity
Spacetime geometry, and therefore gravity, emerges from quantum entanglement, analyses using tensor networks show.
-
 Physics
PhysicsUnusual turbulence seen along North Carolina coast
Storm winds in Currituck Sound, North Carolina, may have created just the right conditions for scientists to see a rare type of turbulence in ocean waves for the first time.