Physics
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsProposed experiment would create matter from light
Photon collider would convert light into electrons and positrons.
By Andrew Grant -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceRecyclable superplastics made with old chemistry
A new durable plastic and a self-healing gel are the first high-performance polymers that are easily recycled.
By Beth Mole -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsNext-gen quantum teleportation in just 2 photons
Researchers teleport quantum information between two photons instead of the standard three.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
PhysicsGravity’s Ghost and Big Dog
Sociologist Harry Collins chronicles the occasionally heated (and often arcane) debates among scientists studying gravitational waves.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryElement 117 earns spot on periodic table
Atoms jam-packed with 117 protons have been produced at a particle collider in Germany, confirming the discovery of a new element.
-

-
 Chemistry
ChemistryColor-changing polymer maps fingerprints
Tiny beads of sweat may offer new way to identify people’s fingerprints.
By Meghan Rosen -
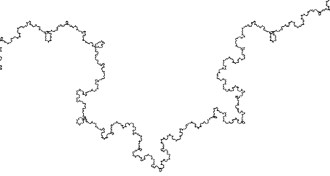 Materials Science
Materials ScienceHow fractals jam glassy materials
Understanding the intricate energy landscape of glasses could help to explain what happens when glassy materials are deformed or when coffee beans in a container jam.
-
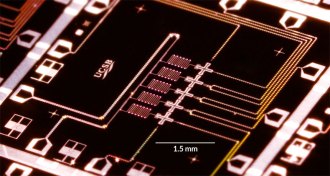 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsMajor step taken toward error-free computing
Physicists have achieved nearly perfect control over a bit of quantum information, bringing them a step closer to error-free computation.
-
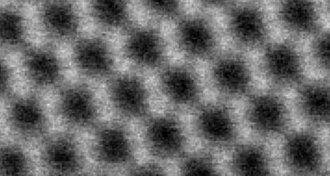 Materials Science
Materials ScienceBlender whips up graphene
Easy recipe makes large quantities of graphene using kitchen blender.
By Beth Mole -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsShor’s code-breaking algorithm inspired reflections on quantum information
Twenty years ago, physicists met in Santa Fe to explore the ramifications of quantum information.
-
 Physics
PhysicsLaser kicks molecules into fastest ever spin
The powerful kick of a laser has spun molecules faster than they’ve ever been spun before: 10 trillion rotations per second, or 600 trillion RPM.
By Andrew Grant