Space
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHow radio astronomy put new eyes on the cosmos
A century ago, radio astronomy didn’t exist. But since the 1930s, it has uncovered cosmic secrets from planets next door and the faint glow of the universe’s beginnings.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNew ideas on what makes a planet habitable could reshape the search for life
New definitions of “habitable worlds” could include planets with global oceans under a steamy hydrogen atmosphere or exclude ones that started out habitable but lost all their water.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary Science50 years ago, astronomers were chipping away at Pluto’s mass
Prior to the discovery of Pluto’s moon Charon, astronomers struggled to pin down the dwarf planet’s mass.
-
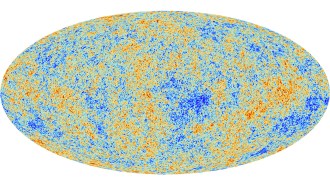 Cosmology
Cosmology‘Flashes of Creation’ recounts the Big Bang theory’s origin story
In ‘Flashes of Creation,’ author Paul Halpern tells the story of George Gamow , Fred Hoyle and their decades-long sparring match about the Big Bang.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe definition of planet is still a sore point – especially among Pluto fans
In the 15 years since Pluto lost its planet status, scientists have continued to use the definition that works for them.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHere’s how cool a star can be and still achieve lasting success
The dividing line between successful stars and failed ones is a surface temperature of about 1,200° to 1,400° Celsius, a new study reports.
By Ken Croswell -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSee some of the most intriguing photos from NASA’s Perseverance rover so far
Six months ago, Perseverance landed on the Red Planet. Here’s what the rover has been observing.
-
 Space
SpaceVera Rubin’s work on dark matter led to a paradigm shift in cosmology
‘Bright Galaxies, Dark Matter, and Beyond’ tells the story of how astronomer Vera Rubin provided key evidence for the existence of dark matter.
-
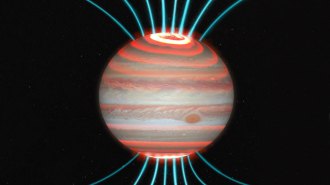 Space
SpaceJupiter’s intense auroras superheat its upper atmosphere
Jupiter’s hotter-than-expected upper atmosphere may be caused by high-speed charged particles slamming into the air high above the poles.
By Sid Perkins -
 Astronomy
AstronomyMeasuring a black hole’s mass isn’t easy. A new technique could change that
The timing of flickers in the gas and dust in a black hole’s accretion disk correlates to its mass, a new study finds.
-
 Space
SpaceA lunar magnetic field may have lasted for only a short time
New analyses of Apollo-era lunar rocks suggest that any magnetosphere that the moon ever had endured for no more than 500 million years.
-
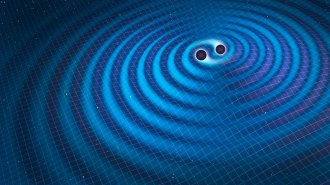 Physics
PhysicsA bounty of potential gravitational wave events hints at exciting possibilities
Of about 1,200 possible events, most are probably false alarms, but some could be ripples in spacetime that are especially hard to spot.