Space
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHow massive stars in binary systems turn into carbon factories
A massive star with an orbiting partner star ejects on average twice as much carbon, an element crucial for life, into space compared with a solo star.
By Ken Croswell -
 Space
SpaceAn ancient exploding comet may explain why glass litters part of Chile
A 75-kilometer-long corridor of chunks of glass in the Atacama Desert probably formed when a comet exploded 12,000 years ago, a study finds.
By Freda Kreier -
 Astronomy
AstronomyDistant rocky planets may have exotic chemical makeups that don’t resemble Earth’s
Elements sprinkled on white dwarf stars suggest that the mantles of faraway rocky worlds differ greatly from their counterparts in our solar system.
By Ken Croswell -
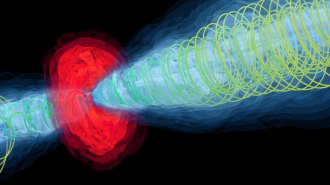 Space
SpaceA stunning simulation re-creates how M87’s black hole launches plasma jets
Two jets, thousands of light-years long, are re-created in a computer simulation, which suggests that M87’s black hole must be spinning rapidly.
-
 Space
SpaceHere’s what the next 10 years of space science could look like
In the latest Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, astronomers have their sights set on a whole fleet of next-generation space telescopes.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNeutron star collisions probably make more gold than other cosmic smashups
Smashups of two neutron stars produce more heavy elements than when a black hole swallows a neutron star, calculations suggest.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePluto’s dark side reveals clues to its atmosphere and frost cycles
Light from Pluto’s moon Charon illuminated the dwarf planet’s farside offering clues about how nitrogen cycles between its surface and its atmosphere.
-
 Space
SpaceA rush to watch a supernova exposed its last gasp before exploding
By studying the final years of stars, scientists hope to find clues to help them recognize when other stars are about to blow.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceWhat the Perseverance rover’s quiet landing reveals about meteor strikes on Mars
InSight tried to detect seismic waves created by the arrival of its sister mission, helping scientists uncover how Mars absorbs energy from impacts.
By Freda Kreier -
 Astronomy
AstronomyAstronomers may have spotted the first known exoplanet in another galaxy
The spiral-shaped Whirlpool galaxy may be the host of the first planet spotted outside of the Milky Way.
-
 Space
Space5 cool things to know about NASA’s Lucy mission to the Trojan asteroids
NASA’s Lucy is the first spacecraft to head to the two giant clumps of space rocks that tag along in Jupiter’s orbit.
-
 Earth
EarthEarth is reflecting less light. It’s not clear if that’s a trend
A decrease in Earth’s reflectance shows our planet is absorbing more solar radiation, but it’s not clear if the trend will last.
By Sid Perkins