All Stories
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMars was habitable longer, more recently than thought
Warmer, wetter conditions lasted until 3.5 billion years ago on the Red Planet.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsGrizzly bears get stressed from salmon decline
Grizzlies in coastal British Columbia bulk up on salmon in the fall, but they experience stress when the fish are scarce.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA corsage that bites
The orchid mantis uses a flowery subterfuge to lure prey.
By Susan Milius -
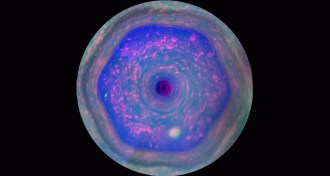 Astronomy
AstronomySaturn’s six-sided cloud pattern gets a close look
New images show particles in the planet’s hexagonally shaped jet stream.
-
 Math
MathTwin primes and prime bunches in mathematicians’ crosshairs
For second time this year, a mathematician makes a major advance toward proving a long-standing conjecture.
-
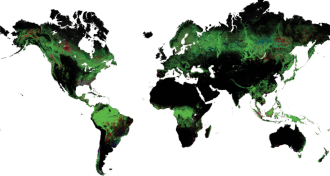 Ecosystems
EcosystemsOnline map tracks forest shifts from space
By layering more than 650,000 satellite images onto a Google map, researchers have created a new tool to track forest cover.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsDazzle camouflage may fool a locust
The bold zig-zag patterns that adorned naval ships during the world wars also appear in nature and may bewilder locusts, a new study suggests.
-
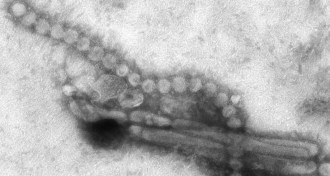 Life
LifeH7N9 flu still better adapted to infect birds over humans
The proteins from the avian flu appear better suited for attaching to bird, not human, molecules.
-
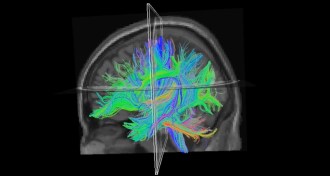 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFaulty brain wiring may contribute to dyslexia
Adults with the disorder showed difficulty transmitting information among areas that process language.
By Beth Mole -
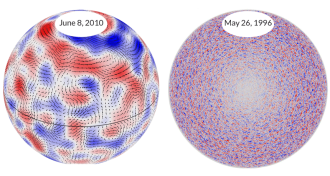 Astronomy
AstronomySun’s rotation driven by enormous plasma flows
Long-lasting plasma flows 15 times the diameter of Earth transport heat from the sun’s depths to its surface, helping explain solar rotation.
-
 Life
LifeAutism may have link to chemicals made by gut microbes
Beneficial bacteria improved abnormal behaviors in mice with altered intestines.
-
 Life
LifeTargeting single set of nerve cells may block mosquitoes
The insects use the same neurons to detect carbon dioxide from our breath and odors from our skin so blocking those cells could lead to more simplified repellent systems.