All Stories
-
 Psychology
PsychologyThe Tell
The Little Clues That Reveal Big Truths About Who We Are by Matthew Hertenstein.
By Sid Perkins -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTV linked with brain changes in kids
A new study of Japanese children gives more reasons not to park kids in front of the tube.
-
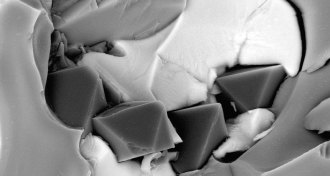 Earth
EarthEarth’s plate boundaries may nurture diamond formation
An experiment mimicking conditions deep in the Earth suggests that some tectonic plate boundaries may make ideal diamond nurseries.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryKeeping wine fine for a longer time
Trace metals in wine can be oxidized, producing browning and a nasty smell. A new study shows how we might be able to keep wine fine using chelators. The catch? You may not be able to drink it.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceChina’s first moon-landing mission blasts off
If successful, the Chang’e 3 lunar lander and Yutu rover will be the first spacecraft to land on the moon in 37 years.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow koalas sing low
Extra set of vocal cords lets males hit surprisingly low notes.
By Beth Mole -
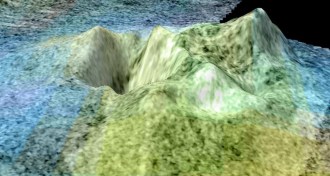 Earth
EarthCryovolcano
An ice volcano that erupts slurries of volatile compounds such as water or methane instead of lava.
By Erin Wayman -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFear can be inherited
Parents’ and even grandparents’ experiences echo in offspring, a study of mice finds.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceTurbulent ocean could explain Europa’s chaotic ice
New computer simulations show turbulent global ocean currents that distribute heat unevenly and could explain the formation of the chaotic ice patterns at the moon’s lower latitudes.
-
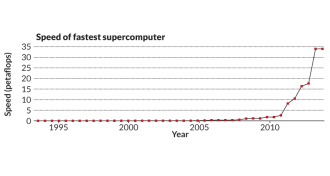 Computing
ComputingFastest supercomputers
The new list of the world’s fastest computers, now in its 20th year, has China’s Tianhe-2 on top with a processing speed of 33.9 petaflops — or quadrillions of calculations per second.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsHiggs boson tale wins book prize
The Particle at the End of the Universe by Sean Carroll.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCancer vaccine in near future foreseen
Excerpt from the December 21, 1963 issue of SCIENCE NEWS LETTER.