All Stories
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMoon’s lava tubes could be colossal
Lava tubes inside the moon could remain structurally sound up to 5 kilometers across and offer prime real estate for lunar colonists.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGenome clues help explain the strange life of seahorses
Researchers have decoded the genetic instruction manual of a seahorse (Hippocampus comes) and found clues to its nearly 104-million-year evolutionary history.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBirth defects occur in 1 in 10 pregnancies with first trimester Zika infection
About 6 percent of U.S. women infected with Zika virus have infants or fetuses with birth defects, according to preliminary CDC results. For women infected in the first trimester, the number is even higher: nearly 11 percent.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Climate
ClimateArctic kelp forests may create summer refuges from ocean acidification
Long summer daylight revs up carbon capture in Arctic kelp forests, offering a little relief from acidifying ocean water.
By Susan Milius -
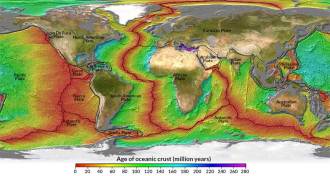 Earth
EarthEarth’s mantle is cooling faster than expected
The thinning of newly formed oceanic crust suggests that Earth’s mantle is cooling much faster than previously thought.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe year of gravitational waves, Zika and more
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses the top science news stories of 2016.
By Eva Emerson -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyTop 10 science stories of 2016: Gravitational waves, Zika, Proxima b and more
The detection of gravitational waves takes the top spot in our top 10 stories of 2016. Also on the list: Zika’s devastation, a nearby exoplanet discovery and more.
-
 Physics
PhysicsYear in review: Gravitational waves offer new cosmic views
The first direct detection of gravitational waves will open a new window on black holes and introduce a new era in astronomy.
-
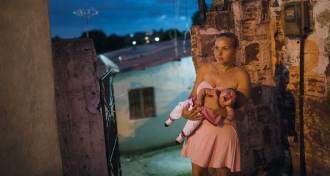 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYear in review: Zika virus devastates Brazil and spreads fear across Americas
The increase in microcephaly in Brazil has spread fear of Zika infection across the Americas.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Astronomy
AstronomyYear in review: A planet lurks around the star next door
If people ever travel beyond the solar system, the newly discovered exoplanet around Proxima Centauri is likely to be a first stop.
-
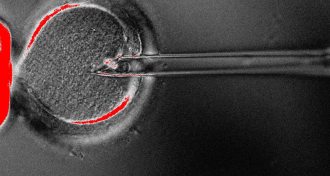 Genetics
GeneticsYear in review: ‘Three-parent baby’ technique raises hope and concern
Safety and ethical concerns surround controversial mitochondrial replacement therapy.
-
 Climate
ClimateYear in review: Sea ice loss will shake up ecosystems
Researchers are studying the complex biological consequences of polar melting and opening Arctic passageways.
By Susan Milius