All Stories
-
 Earth
EarthData show no sign of methane boost from thawing permafrost
Rapid Arctic warming has increased emissions of carbon dioxide, but not methane, from northern Alaska tundra.
-
 Neuroscience
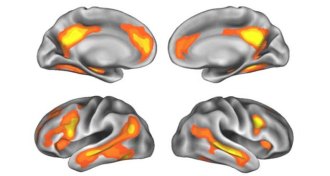
NeurosciencePregnancy linked to long-term changes in mom’s brain
Pregnancy can sculpt a mother’s brain in a way that may help her tune in to her baby.
-
 Physics
PhysicsAntimatter hydrogen passes symmetry test
Antihydrogen atoms behave similarly to normal hydrogen atoms.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMonkeys have vocal tools, but not brains, to talk like humans
Macaques have vocal tracts, but not brains, built for talking much as people do, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyScience News’ favorite books of 2016
Science News writers and editors compiled a list of the books they were most excited about this year.
-
 Tech
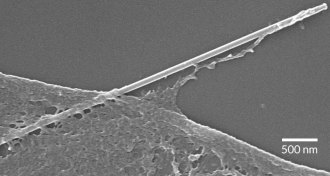
TechCells snack on nanowires
Human cells eat silicon nanowires in a process called phagocytosis. Nanowire-infused cells could be a step towards biological electronic devices.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyNew footprint finds suggest range of body sizes for Lucy’s species
Tracks discovered in Tanzania appear to have belonged to the tallest known Australopithecus afarensis individual, but stature estimates can be tricky.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsChimps look at behinds the way we look at faces
Humans demonstrate something called the inversion effect when gazing at faces. Chimpanzees do this too — when looking at other chimps’ butts.
-
 Genetics
Genetics50 years ago, alcohol use was linked to several gene variants
50 years later, scientists are still searching for genes that influence drinking.
-
 Earth
EarthMegadiamonds point to metal in mantle
Imperfections in supersized diamonds hint at metallic iron and nickel in Earth’s mantle.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceDawn spacecraft maps water beneath the surface of Ceres
Water ice sits just beneath the surface and within some permanently shadowed craters of the dwarf planet Ceres.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsProteins that reprogram cells can turn back mice’s aging clock
Proteins that reprogram adult cells to an embryonic-like state can rejuvenate prematurely aging mice.