All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMath offers new view of brain and its disorders
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses new insights into the brain's role in mental illness, sleep, and ancient rituals.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika, psychobiotics and more in reader feedback
Readers respond to the April 2, 2016, issue of Science News with thoughts on Zika virus, planetary science, microbes in mental health and more.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe bizarre mating ritual of a bee parasite
Stylops ovinae insects — parasites found in mining bees — have short lives filled with trauma.
-
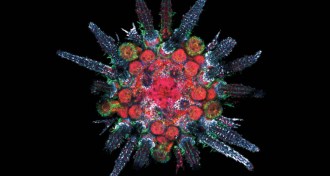 Animals
AnimalsSome animals ‘see’ the world through oddball eyes
Purple urchins, aka crawling eyeballs, are just one of several bizarre visual systems broadening scientists’ view of what makes an eye.
By Susan Milius -
 Agriculture
AgricultureNew analysis: Genetically engineered foods not a health risk
No real evidence for health or environmental dangers of GE crops.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWith easy e-cig access, teen vaping soars
The vast majority of U.S. states ban sales or distribution of e-cigarette products to minors. Still, it’s no sweat for teens to buy them online.
By Janet Raloff -
 Life
LifeHow the Galápagos cormorant got its tiny wings
Galápagos cormorants’ tiny wings may be due to altered reception in cellular antennas.
-
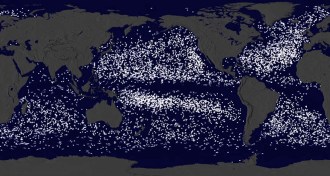 Oceans
OceansHere’s where 17,000 ocean research buoys ended up
A combined look at 35 years’ worth of ocean buoy movements reveals the currents that feed into ocean garbage patches.
-
 Life
LifeGiraffe’s long neck linked to its genetic profile
Giraffes’ genes may reveal how their necks grew long and hearts got strong.
-
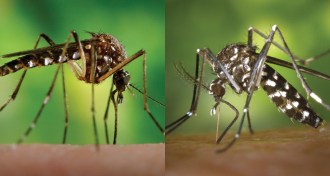 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists wrestle with possibility of second Zika-spreading mosquito
It’s hard to say yet whether Asian tiger mosquitoes will worsen the ongoing Zika outbreak in the Americas.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
Animals‘America’s Snake’ chronicles life and times of iconic timber rattlesnake
America’s Snake looks past timber rattlesnake’s fearsome reputation and delves into the fascinating biology of this iconic serpent.
By Sid Perkins -
 Astronomy
AstronomyFast-moving star duo is heading out of the Milky Way
A pair of hyperfast stars hurtling through a remote region of the Milky Way might have been orphaned after a long-ago galactic collision, a new study suggests.