All Stories
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSeismic experiment might reveal thickness of Europa’s ice
Crashing an empty rocket fuel tank into the surface of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, could help scientists figure out the thickness of the ice.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeWomen in sports are often underrepresented in science
More and more women are taking up recreational and competitive sports. But when it comes to exercise science, the studies don’t reflect that trend.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAntibiotics in cattle leave their mark in dung
Treating cattle with antibiotics may have side effects for dung beetles, microbes and greenhouse gases.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSnot could be crucial to dolphin echolocation
An acoustic model reveals that echolocation relies on mucus lined tissue lumps in the animal’s nasal passage.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyReturn of superstar supernova raises doubt about its identity
The brightest supernova on record is back for round two, and might not be a supernova after all.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSpace experts say sending humans to Mars worth the risk
At a meeting in Washington, NASA and aerospace reps discuss the hopes and hurdles of landing a crew on Mars by the 2030s.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineResearchers face off over whether newborns are really copycats
Scientists disagree about whether babies can imitate movements and facial expressions shortly after birth.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyEvidence of 5,000-year-old beer recipe found in China
Ancient brewer’s toolkits put barley on tap in China as early as 3400 B.C.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThe center of Earth is younger than the outer surface
Einstein’s general theory of relativity predicts the center of the Earth is two years younger than the crust.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyYoung sun’s super solar flares helped set early Earth up for life
Super solar flares may have provided early Earth with planet-warming and life-building molecules.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor baby sea turtles, it helps to have a lot of siblings
After hatching, baby sea turtles must dig themselves out of their nest. This requires less energy if there are lots of siblings, a new study finds.
-
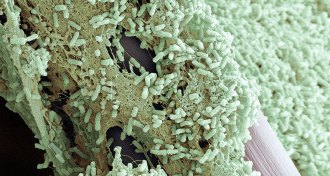 Life
LifeScientists find way to break through bad bacteria’s defenses
Enzymes can break down bacterial biofilm’s sugary walls.