All Stories
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBubbles may have sheltered Earth’s early life
Bubbles formed on ancient shorelines offer scientists a new place to look for traces of early life.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Tech
TechSpaceX rocket sticks its landing
A Falcon 9 rocket section lands after launching a set of satellites during a successful test of SpaceX’s reusable rocket parts.
-
 Tech
TechSpaceX rocket blasts to space and back, sticks the landing
A Falcon 9 rocket section lands after launching a set of satellites during a successful test of SpaceX’s reusable rocket parts.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyIn science, a lack of replication shouldn’t kill your reputation
The proof is science is when a study is replicated. When it’s not, do scientists suffer? A new study says researchers may overestimate the negative effects.
-
 Health & Medicine
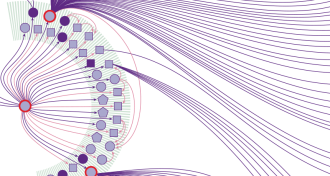
Health & MedicineAnatomy of the South Korean MERS outbreak
The Middle East respiratory syndrome virus, which infected 186 people in South Korea in 2015, quickly spread within and between hospitals via a handful of “superspreaders.”
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCow bites and spacecraft injuries enliven new medical diagnostic codes
The 10th edition of International Classification of Diseases went into effect in 2015, and it included some interesting additions.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
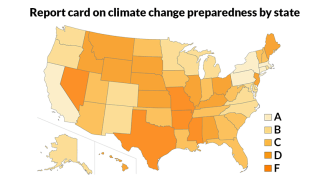
ClimateReport card shows which states are best prepared for climate change
A preparedness report card shows that some states aren’t ready for the extreme heat, droughts, wildfires and flooding that may come with climate change.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyExoplanets need right stuff to be habitable
The elemental makeup of a star can reveal whether planets in its solar system could support sustained plate tectonics, a requirement for Earth-like life, researchers propose.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureNumber of wild bees drops where they’re needed most
Wild bee abundance in the United States is lowest in agricultural regions, according to a new model.
-
 Life
LifeTweaking the pattern equations
A more than 60-year-old theory about how patterns in nature form gets an update.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyScience News’ favorite books of 2015
The Science News staff offers its must-read picks of 2015.
-
 Earth
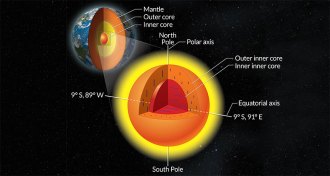
EarthSolid inner, inner core may be relic of Earth’s earliest days
Earth’s innermost inner core may have formed billions of years earlier than previously thought, shortly after the planet’s accretion.