All Stories
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCrops take up drugs from recycled water
Plants irrigated with recycled wastewater can soak up tiny amounts of pharmaceutical compounds but what this means for human health is unclear.
By Beth Mole -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceFeedback
Readers discuss sources of stress in everyday life and tell us what they think about NASA's plan to nab an asteroid.
-
 Life
LifeThoughtful approach to antibiotic resistance
Changing how people think about antibiotics is already showing promise in reducing antibiotic use and costs. It’s doubtful, however, that any single strategy will be enough.
By Eva Emerson -
 Paleontology
Paleontology3-D scans reveal secrets of extinct creatures
Paleontologists can dig into fossils without destroying them and see what’s inside using 3-D scanning. What they’re learning helps bring the past to life.
-
 Plants
PlantsBorrowed genes raise hopes for fixing “slow and confused” plant enzyme
Inserting some bacterial Rubisco chemistry into a plant might one day boost photosynthesis and help raise crop yields.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBanana peel slipperiness wins IgNobel prize in physics
Cartoons taught us that banana peels make for a slick trip to the floor, but scientists decided to find out just how slippery they could be.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDoctors enlisted to turn the tide on antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic stewardship requires education, diligence, and changes in prescribing. At some hospitals, it’s beginning to halt a dangerous trend.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNot all the ‘baby friendly’ rules are rooted in science
The Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative has a noble goal of encouraging breastfeeding, but some of its recommendations may be based on shaky science.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyEnormous black hole resides at core of tiny galaxy
A small galaxy stores 15 percent of its mass in a black hole, suggesting compact galaxies might be shreds of once larger galaxies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineObama takes aim at antibiotic resistance
The White House offers an incentive for better diagnostics and calls for new meds and more stewardship programs against antibiotic resistance.
-
 Tech
TechLong after JFK assassination, gunshot forensics still limited
The Warren Commission Report included the results of a neutron activation analysis test of Lee Harvey Oswald. But even that high-tech analysis can't distinguish the type of weapon fired.
-
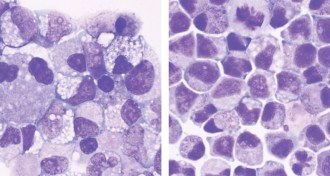 Life
LifeMolecule boosts numbers of stem cells in umbilical cord blood
A new molecule multiplies stem cells in umbilical cord blood. More blood-making stem cells could mean more effective transplants for people with blood cancers.