All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGrowth in diabetes diagnoses starting to slow in U.S.
The percentage of the population diagnosed with diabetes and the rate of new cases per year rose sharply between 1990 and 2008 but haven't grown quite as quickly between 2008 and 2012.
-
 Cosmology
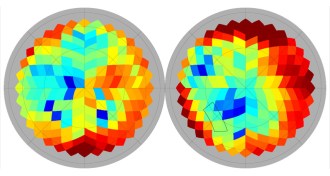
CosmologyGravitational wave discovery gives way to Milky Way dust
New polarization maps from the Planck satellite suggest that the BICEP2 announcement this year of primordial gravitational waves might be due entirely to dust in our galaxy.
-
 Tech
TechHybrid robot merges flier with two snakelike machines
A helicopter robot can airlift snakelike search-and-rescue bots out of tight situations.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStatins may improve odds of surviving a bleeding stroke
Common cholesterol-lowering drugs called statins may help people who have suffered a stroke caused by ruptured blood vessels.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Animals
AnimalsChimps raised among humans may have problems as adults
Chimpanzees taken away from their mothers and raised to be pets or entertainers have problems relating to other chimps later in life.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDyslexic brain may solve some math problems in a roundabout way
Children with dyslexia rely heavily on right brain to do addition problems.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThere’s a new way to quantify structure and complexity
A new way to measure structure and complexity can help explain how information sharing among the parts of a system is related to its behaviors on different scales.
-
 Tech
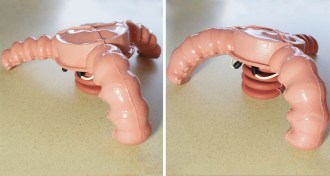
TechHopping robot powered by explosions
A soft-bodied robot that can jump with the help of an explosion could one day aid search-and-rescue operations.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMAVEN spacecraft set to explore Martian atmosphere
The Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft entered into orbit around the Red Planet on September 21.
-
 Earth
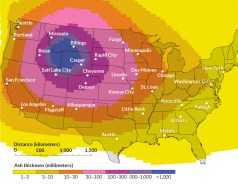
EarthSupervolcano blast would blanket U.S. in ash
A new simulation illustrates the explosiveness of the volcano that lurks beneath Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Fantastic Lab’ recounts battle against typhus, Nazis
Arthur Allen explores how two European scientists produced typhus vaccines during World War II.
-
 Ecosystems
Ecosystems‘Where Do Camels Belong?’ explores invasive species
Ecologist Ken Thompson takes a closer look at the impacts (or lack thereof) of invasive species.