News
-
 Life
LifeThis ancient worm might be an important evolutionary missing link
A roughly 520-million-year-old fossil may be the common ancestor of a diverse collection of marine invertebrates.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDrone photos reveal an early Mesopotamian city made of marsh islands
Urban growth around 4,600 years ago, near what is now southern Iraq, occurred on marshy outposts that lacked a city center.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaur ‘mummies’ may not be rare flukes after all
Bite marks on a fossilized dinosaur upend the idea that exquisite skin preservation must result from a carcass's immediate smothering under sediment.
By Jake Buehler -
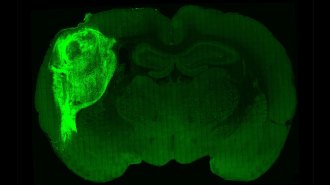 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceClumps of human nerve cells thrived in rat brains
New results suggest that environment matters for the development of brain organoids, 3-D nerve cell clusters that grow and mimic the human brain.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s DART mission successfully shoved an asteroid
Data obtained since the spacecraft intentionally crashed into an asteroid show that the impact altered the space rock’s orbit even more than intended.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe James Webb Space Telescope spied the earliest born stars yet seen
The stars, found in the first released science image from the James Webb Space Telescope, probably winked into existence about 13 billion years ago.
-
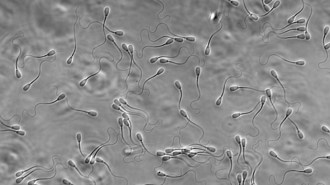 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCooperative sperm outrun loners in the mating race
Sperm that swim in clusters travel more directly toward the uterus, while overcoming fluid currents in the reproductive tract.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhy traumatic brain injuries raise the risk of a second, worse hit
Recent hits to Miami Dolphins quarterback Tua Tagovailoa have reignited discussions of brain safety for professional football players. Brain experts weigh in.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMars’ buried ‘lake’ might just be layers of ice and rock
Evidence grows that possible detections of liquid water buried near Mars’ south pole might not hold water.
-
 Life
LifeA metal ion bath may make fibers stronger than spider silk
The work is the latest in a decades-long quest to create artificial fibers as strong, lightweight and biodegradable as spider silk.
By Meghan Rosen -
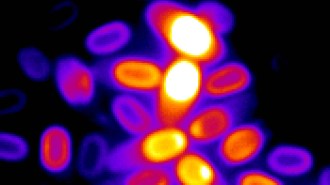 Microbes
MicrobesHow dormant bacteria spores sense when it’s time to come back to life
Bacterial cells shut down and become spores to survive harsh environments. An internal countdown signals when it’s safe for bacteria to revive.
-
 Humans
HumansHere’s where jazz gets its swing
Swing, the feeling of a rhythm in jazz music that compels feet to tap, may arise from near-imperceptible delays in musicians’ timing, a study shows.
By Nikk Ogasa