News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHere’s why humans chose particular groups of stars as constellations
Distances between stars, their brightnesses and patterns of human eye movement explain why particular sets of stars tend to be grouped together.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHow kelp forests off California are responding to an urchin takeover
A pair of studies reports 95 percent loss of kelp forests along the northern coast while sea otters are helping maintain surviving kelp farther south.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyParents in Western countries report the highest levels of burnout
The first survey comparing parental exhaustion across 42 countries links it to a culture of self-reliance.
By Sujata Gupta -
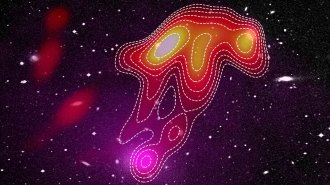 Astronomy
AstronomyThe ‘USS Jellyfish’ emits strange radio waves from a distant galaxy cluster
The unusual pattern of radio waves dubbed the USS Jellyfish tells a story of intergalactic gas meeting black hole by-products.
By Ken Croswell -
 Animals
AnimalsA toxin behind mysterious eagle die-offs may have finally been found
A 20-year study of water weeds and cyanobacteria in the southern United States pinpoints a bird-killing toxin, and it's not your usual suspect.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsA gene defect may make rabbits do handstands instead of hop
Mutations in a gene typically found throughout the nervous system rob rabbits of their ability to hop. Instead, the animals walk on their front paws.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAstraZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccine holds up in an updated analysis of trial data
The redo dropped the overall efficacy of AstraZeneca’s vaccine from 79 percent to 76 percent. But a slight fluctuation is not unexpected, experts say.
-
 Life
LifeA plant gene may have helped whiteflies become a major pest
An agricultural pest may owe part of its success to a plant detox gene it acquired long ago that lets the insect neutralize common defenses.
-
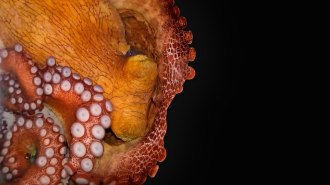 Animals
AnimalsOctopus sleep includes a frenzied, colorful, ‘active’ stage
Four wild cephalopods snoozing in a lab had long stretches of quiet napping followed by brief bursts of REM-like sleep.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow using sheepskin for legal papers may have prevented fraud
Removing fat is key to turning animal skin into parchment. With sheepskin, the process creates a writing surface easily marred by scratched-out words.
-
 Physics
PhysicsAtomic clocks take a step toward redefining the second
Measurements of the clocks’ frequencies provide the most precise clock comparisons yet, with uncertainties less than a quadrillionth of a percent.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA new black hole image reveals the behemoth’s magnetic fields
A new analysis of Event Horizon Telescope data from 2017 brings to light the magnetic fields twisted around the black hole at the core of galaxy M87.