News
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsA new test of water ripples supports the idea of quantum heat in a vacuum
Water waves bolster theory that accelerating space travelers really feel the heat.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnimal goo inspires better glue
Researchers are turning to nature to create adhesives that work in the wet environment of the human body.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyR.I.P. Cassini
After 20 years, nearly 300 orbits and pioneering discoveries, the Cassini spacecraft plunges to its death in Saturn’s atmosphere — taking data until its very last breath.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow to peel permanent marker off glass
Water’s surface tension can peel a thin hydrophobic film such as permanent ink off glass surfaces.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologySkeleton ignites debate over whether women were Viking warriors
Scientists spar over a 10th century woman who may have had serious fight in her.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyLike sea stars, ancient echinoderms nibbled with tiny tube feet
An ancient echinoderm fossil preserves evidence of tube feet like those found on today’s sea stars.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe sun’s strongest flare in 11 years might help explain a solar paradox
The sun tends to release its biggest flares at the ends of solar cycles — and we might finally be able to test why.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyScience can’t forecast love
Scientists’ forecast for romantic matches is unpredictable.
By Bruce Bower -
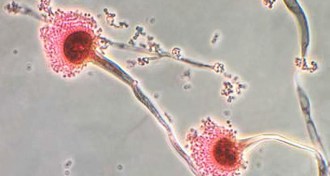 Life
LifeWhen a fungus invades the lungs, immune cells can tell it to self-destruct
Immune system resists fungal infection by directing spores to their death.
-
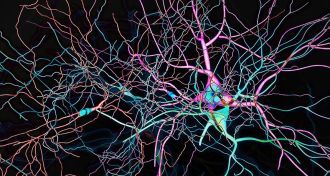 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain chemical lost in Parkinson’s may contribute to its own demise
A dangerous form of the chemical messenger dopamine causes cellular mayhem in the very nerve cells that make it.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyWoolly rhinos may have grown strange extra ribs before going extinct
Ribs attached to neck bones could have signaled trouble for woolly rhinos, a new study suggests.
By Susan Milius -
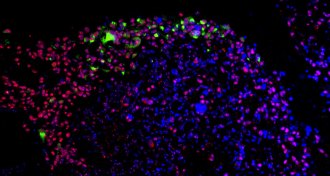 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika could one day help combat deadly brain cancer
The Zika virus targets cells that cause glioblastoma, an aggressive form of brain cancer, studies in human cells and mice show.