News
-
 Life
LifeYeasts hide in many lichen partnerships
Yeasts newly discovered in common lichens challenge more than a century of thinking about what defines the lichen symbiosis.
By Susan Milius -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHumans, birds communicate to collaborate
Bird species takes hunter-gatherers to honeybees’ nests when called on.
By Bruce Bower -
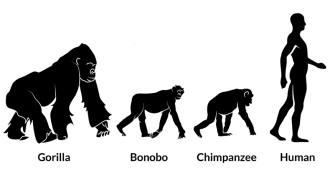 Genetics
GeneticsEvolution of gut bacteria tracks splits in primate species
Primates and microbes have been splitting in sync for at least 10 million years.
-
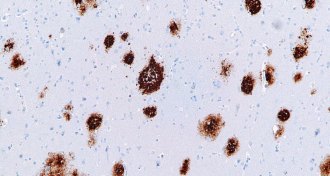 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAntibiotics might fight Alzheimer’s plaques
A new study found that antibiotics hit Alzheimer’s plaques in the brains of mice.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTo douse hot hives, honeybee colonies launch water squadrons
The whole superorganism of a honeybee colony has sophisticated ways of cooling down.
By Susan Milius -
 Physics
PhysicsElectrons have potential for mutual attraction
Electrons usually repel each other, but new research shows pairs of electrons can be attracted due to their repulsion from other electrons.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAnesthesia steals consciousness in stages
Brains regions that are synchronized when awake stop communicating as monkeys drift off.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists throw a curve at knuckleball explanation
Wildly swerving pitches may be the result of a phenomenon known as a “drag crisis”
-
-
 Science & Society
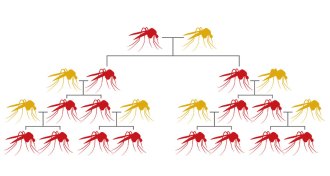
Science & SocietyGM mosquitoes succeed at reducing dengue, company says
GM mosquito releases in Brazil have helped cut dengue cases 91 percent in a year.
By Susan Milius -
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyBlack hole born without stellar parent, evidence suggests
A galaxy in the early universe might harbor the first known “direct collapse” black hole, one that forms when a cloud of gas collapses under its own weight without forming stars.