News
-
 Climate
ClimateIndia’s monsoon winds trace back nearly 13 million years
The intense monsoon winds that carry torrential rain to India each year first started blowing around 12.9 million years ago, new research suggests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient reptiles saw red before turning red
The discovery that birds and turtles share a gene tied to both color vision and red coloration is more evidence that dinosaurs probably saw the color red — and perhaps were even red, too.
-
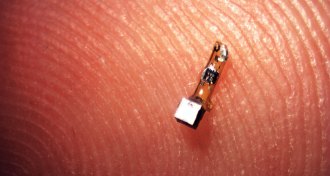 Neuroscience
Neuroscience‘Neural dust’ can listen to body’s electrical signals
Tiny crystals can detect electrical signals in nerves and muscles of rats.
-
 Physics
PhysicsLIGO’s black holes may be dark matter
Two analyses indicate that LIGO could have detected black holes that formed just after the Big Bang.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFDA OKs first GM mosquito trial in U.S. but hurdles remain
The FDA has concluded that test releases of Oxitec GM mosquitoes on a Florida key poses no significant problem for the environment, but local officials still have to agree
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew fossil suggests echolocation evolved early in whales
A 27-million-year-old whale fossil sheds light on echolocation’s beginnings.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsRats offer clues to biology of alcoholism
Heavy-drinking rats are giving scientists new genetic clues to alcoholism.
-
 Earth
EarthChina’s mythical ‘Great Flood’ possibly rooted in real disaster
Folktales of an ancient flood that helped kick off Chinese civilization may reference a nearly 4,000-year-old deluge.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceCeres is more than just a space rock
Dawn spacecraft reveals that the dwarf planet Ceres hides a core of solid rock beneath an outer crust of minerals, salts and ices.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDiversity of indoor insects, spiders adds to life’s luxuries in high-income neighborhoods
A massive survey of indoor spiders and insects in town finds dozens of different scientific families in homes, more in high-income neighborhoods.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceRunning doesn’t make rats forgetful
Running doesn’t seem to wipe out old memories in rats, concludes a new study that contradicts earlier reports suggesting that exercise does actually help old memories fade and new memories form — in other rodents.
By Meghan Rosen -
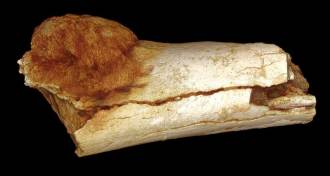 Anthropology
AnthropologyOldest evidence of cancer in human family tree found
Bony growths on fossils may push origins of this disease way back in the Stone Age.
By Bruce Bower