Uncategorized
-
 Space
SpaceBlack hole plasma jets are shaped like bell-bottoms
Jets of high-energy particles change from slightly curved sides to flared cones as they shoot away from galaxies, just like flare-legged pants.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsAn unexpected result from a dark matter experiment may signal new particles
An excess of events spotted in the XENON1T experiment could be signs of solar axions or weird, new properties of neutrinos, but not dark matter itself.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA from a 5,200-year-old Irish tomb hints at ancient royal incest
Ruling families in Ireland may have organized a big tomb project, and inbred, more than 5,000 years ago, a new study suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsMeasuring the neutron’s lifetime from space could solve an enduring mystery
Measurements on Earth show that lone neutrons decay after about 15 minutes, and now scientists have measured that lifetime from space.
-
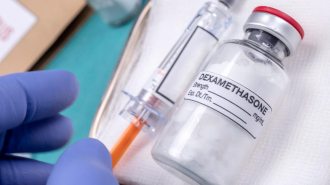 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe steroid dexamethasone is the first drug shown to reduce COVID-19 deaths
The drug might save one of every eight people on ventilators and one of 25 on oxygen.
-
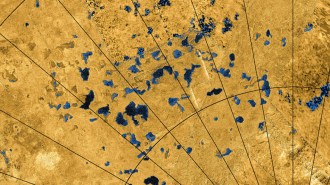 Space
SpaceFlat spots on Saturn’s moon Titan may be the floors of ancient lake beds
Bright radio signals from Titan indicate the presence of ancient lake beds in its tropics, a new analysis finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 lockdowns helped people get more, but not necessarily better, sleep
Two studies report that people began sleeping more and more regularly after countries imposed stay-at-home orders to slow the coronavirus’ spread.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBarn owlets share food with their younger siblings in exchange for grooming
Scientists weren’t sure why elder barn owlets would give away meals to their younger kin, a rare example of sibling cooperation in birds.
By Pratik Pawar -
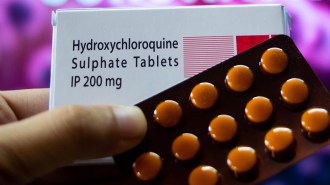 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe FDA has canceled emergency use of hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19
The malaria drug is unlikely to work as an antiviral and its risks don’t outweigh benefits in use against the coronavirus, the agency rules.
-
 Earth
EarthSmoke from Australian fires rose higher into the ozone layer than ever before
The catastrophic wildfires in Australia around New Year’s generated a massive smoke plume that still hasn’t dissipated in the stratosphere.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLarvaceans’ underwater ‘snot palaces’ boast elaborate plumbing
Mucus houses have valves and ducts galore that help giant larvaceans extract food from seawater.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyReal-life scientists inspire these comic book superheroes
Three scientists are publishing comics casting researchers as heroes, and hope the cartoon format and pared-down storyline can boost science literacy.
By Kyle Plantz