Uncategorized
-
 Tech
Tech1960s research paid off in automotive safety
Scientists in 1964 were studying shatterproof glass, which was mandated just a couple of years later.
-
 Health & Medicine
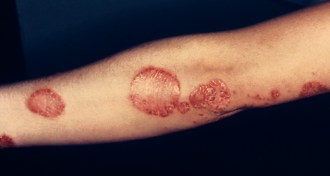
Health & MedicineTwo genes clear up psoriasis and eczema confusion
Psoriasis and eczema are often mistaken for each other, leading to mistreatment. Testing just two genes could eliminate this confusion.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Life
LifeGecko adhesion takes electric turn
Challenging a favored theory, measurements suggest that electrostatic interactions make gecko feet supersticky.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDuck-billed dinosaurs roamed the Arctic in herds
Young and old duck-billed dinosaurs lived together in herds in the Arctic, tracks preserved in Alaska indicate.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Astronomy
AstronomySupernova rapidly creates dust between stars
Astronomers watch a shell of dust form within weeks of a star’s explosion.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossils reveal largest airborne bird
Despite its massive size, an extinct bird may have been an efficient glider.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMicroplastics lodge in crab gills and guts
Crabs can absorb microplastic particles through their gills and by eating polluted mussels.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Earth
EarthGravity variations foretell flood risk months in advance
Tiny gravitational tugs from saturated river basins allow NASA satellites to forecast flood risk.
-
 Life
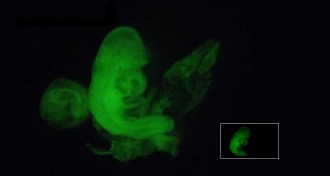
LifeDramatic retraction adds to questions about stem cell research
Researchers who reported an easy method for making stem cells admit mistakes mar their work, and have retracted their papers from Nature.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyRare planet circles just one of a pair of stars
A newly discovered exoplanet orbits one star in a binary pair and shows that planets can form even with a second sun nearby.
-
 Earth
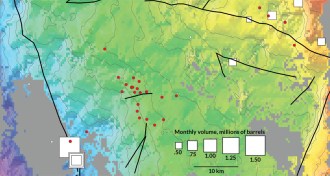
EarthOklahoma earthquakes triggered by wastewater injection
Dumping wastewater from the oil and gas industry into disposal wells may have set off swarm of earthquakes in Oklahoma.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Astronomy
AstronomyExoplanets once trumpeted as life-friendly may not exist
Two exoplanets considered among the most promising for hosting life may not exist, a new study suggests.
By Andrew Grant