
Senior physics writer Emily Conover joined Science News in 2016. She has a Ph.D. in physics from the University of Chicago, where she studied the weird ways of neutrinos, tiny elementary particles that can zip straight through the Earth. She got her first taste of science writing as a AAAS Mass Media Fellow for the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. She has previously written for Science Magazine and the American Physical Society. She is a two-time winner of the D.C. Science Writers’ Association Newsbrief award, and a winner of the Acoustical Society of America’s Science Communication Award.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Emily Conover
-
 Physics
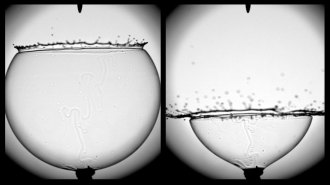
PhysicsListening to soap bubbles pop reveals the physics behind the bursts
The quiet, high-pitched sound made by a popping soap bubble reveals the forces that occur during the bubble’s demise.
-
 Space
SpaceNASA icon Katherine Johnson has died at the age of 101
The “Hidden Figure” captured the public’s admiration after the story of her career was publicized in a 2016 book and film.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThis fundamental constant of nature remains the same even near a black hole
A number that sets the strength of electromagnetic interactions isn’t altered by the extreme gravity around the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsAntimatter hydrogen has the same quantum quirk as normal hydrogen
Atoms of antihydrogen are affected by the Lamb shift, which results from transient particles appearing and disappearing.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThe fastest way to heat certain materials may be to cool them first
A theoretical study reveals that, in certain situations, some materials might heat up more quickly after first being cooled.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsScientists entangled quantum memories linked over long distances
The entanglement of quantum ‘hard drives’ is a crucial step toward creating a quantum internet.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow to make the best fried rice, according to physics
Researchers show exactly how rocking and sliding a wok can launch fried rice into the air, letting it cook at a high temperature without burning.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA barrier to colliding particles called muons has been smashed
Future particle accelerators could slam muons together to reach higher energies than any before.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsMisbehaving kaons could hint at the existence of new particles
Certain extremely rare decays seem to be happening more often than expected, and scientists don’t know why.
-
 Physics
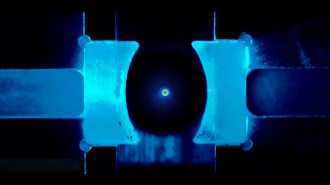
PhysicsScientists cooled a nanoparticle to the quantum limit
Physicists decreased a nanoparticle’s motion to the lowest level allowed by quantum mechanics.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA quantum strategy could verify the solutions to unsolvable problems — in theory
A quantum technique for verifying solutions to difficult problems could apply to an “unbelievably huge” class of puzzles.
-
 Chemistry
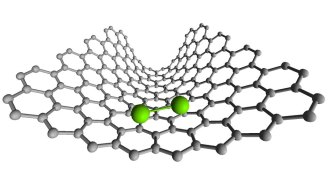
ChemistryA dance of two atoms reveals chemical bonds forming and breaking
Two rhenium atoms approach and retreat from one another in an electron microscope video.