Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Physics
PhysicsRogue waves don’t always appear unannounced
Scientists may be able to forecast the arrival of anomalously large ocean swells, suggest scientists who analyzed the moments before rogue water waves and freak light flashes.
By Andrew Grant -
 Climate
ClimateReal estate is tight as marine species move to cooler waters
Marine species migrating amid global warming face shrinking habitats in cooler locations.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
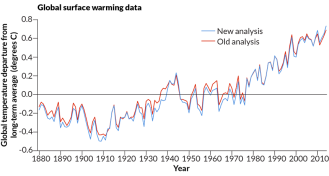
ClimateGlobal warming ‘hiatus’ just an artifact, study finds
Skewed data may have caused the appearance of the recent global warming hiatus, new research suggests.
-
 Earth
EarthEruptions create new islands in the Red Sea
Satellite maps reveal the formation of two new volcanic islands in the Red Sea.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMystery toxins in tainted New Zealand honey nabbed
Sweet and stealthy toxins have been caught sticky-handed, potentially solving a decades-long mystery of tainted honey in New Zealand.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateTitanic typhoons are in the forecast
Warming subsurface water in the Pacific will boost average typhoon intensity 14 percent by 2100, new research predicts.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWealth of cephalopod research lost in a 19th century shipwreck
Nineteenth-century scientist Jeanne Villepreux-Power sent her research papers and equipment on a ship that sank off the coast of France, submerging years’ worth of observations on cephalopods.
-
 Climate
ClimateEverest could lose most of its ice by the end of the century
Glaciers around Mt. Everest will lost most of their ice by the end of the century, new research predicts.
-
 Climate
ClimateEverest could lose most of its ice by 2100
The Everest region of the Himalayas could lose 73 to 96 percent of its ice by 2100, new research predicts.
-
 Climate
ClimateNext icy era may be on hold
Carbon emissions from humans may have postponed Earth’s next glaciation, new research suggests.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentRising dolphin deaths linked to Deepwater Horizon spill
Lung lesions and other injuries link an extensive die-off of dolphins in the Gulf of Mexico to the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateTranquil ecosystems may explain wild swings in carbon dioxide stashing
Semiarid ecosystems, such as grasslands and shrublands, are behind the large variation in the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide sucked in by land each year.
By Beth Mole