Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
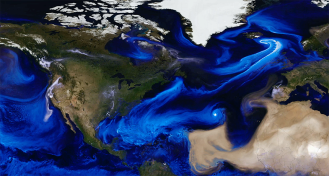 Earth
EarthWatch NASA’s mesmerizing new visualization of the 2017 hurricane season
Swirls of sand, sea salt and smoke make atmospheric currents visible in a new NASA visualization.
-
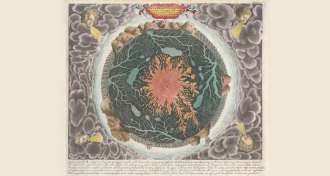 Science & Society
Science & SocietyA new map exhibit documents evolving views of Earth’s interior
"Beneath Our Feet" puts maps on display to show how people have envisioned and explored Earth’s subsurface.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe key to breaking down plastic may be in caterpillars’ guts
Caterpillars that feast on plastic have different gut microbes than those that eat a grain-based diet.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHoneybees fumble their way to blueberry pollination
Blueberry flowers drive honeybees to grappling, even stomping a leg or two down a bloom throat, to reach pollen.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsEPA OKs first living pest-control mosquito for use in United States
Feds approve non-GM male tiger mosquitoes for sale as fake dads to suppress local pests.
By Susan Milius -
 Climate
ClimateHumans are driving climate change, federal scientists say
Human influence “extremely likely” to be dominant cause of warming in last 70 years, U.S. climate report finds.
-
 Earth
EarthDino-dooming asteroid impact created a chilling sulfur cloud
The Chicxulub impact spewed more sulfur than previously believed.
-
 Earth
EarthWind may be driving the melting of East Antarctica’s largest glacier
Winds may be helping warm ocean waters speed up the melting of East Antarctica’s largest glacier.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s the real story on jellyfish taking over the world
In 'Spineless,' a former marine scientist reconnects with the seas and science through her obsession with these enigmatic creatures.
-
 Earth
EarthA deadly 2014 landslide’s power came from soils weakened by past slides
Researchers reconstruct how a hillside failed, producing the deadly 2014 Oso landslide.
-
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change may threaten these bamboo-eating lemurs
Longer dry spells and more nutrient-poor bamboo might eventually doom the greater bamboo lemur, a critically endangered species.
By Susan Milius -
 Climate
ClimateAs ice retreats, frozen mosses emerge to tell climate change tale
Plants long entombed beneath Canadian ice are now emerging, telling a story of warming unprecedented in the history of human civilization.