Health & Medicine
-

-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDextrose rub helps newborns with low blood sugar
Massaging the sugary gel into babies’ mouths may lessen the need for intravenous infusions of glucose, a study shows.
By Nathan Seppa -

-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHome births more risky than hospital deliveries
Babies born at home are more likely to lack pulse after five minutes.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Animals
AnimalsMERS virus jumped several times from animals to humans
More than one person caught new illness from bats, camels or other creatures.
-
 Humans
HumansBrain research goals laid out
NIH details priority areas, including improving imaging technology and mapping brain structures.
-
 Humans
HumansChemical behind corked wine quashes other aromas
Old sock smell signals contamination but doesn't belong to TCA, study proposes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAlzheimer’s disease protein structure may vary among patients
Two people with different symptoms had amyloid-beta fibers with different shapes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaccine stops deadly sand-fly-spread scourge in animal test
A DNA vaccine triggers protection against the sand-fly-borne scourge Leishmania.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSzechuan pepper taps at nerve fibers
The spice makes lips tingle at 50 beats per second, researchers find.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFructose may be key to weight gain
Mice that could not make or metabolize the sugar gained less weight than normal mice.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
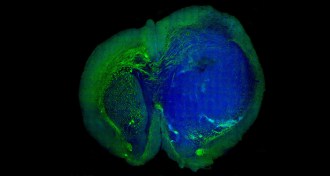
Health & MedicineDevice offers promise of no brain tumor left behind
A new technique might allow surgeons to identify with precision where brain cancer ends and healthy tissue begins.
By Nathan Seppa