Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAn ancient social safety net in Africa was built on beads
A Stone Age network of communities across southern Africans was established using ostrich shell beads by around 33,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
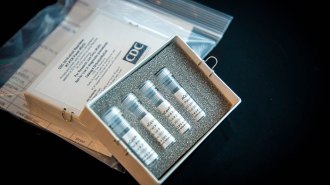 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat you need to know about coronavirus testing in the U.S.
Testing for the new coronavirus is still limited but could ramp up soon, thanks in part to tests developed by state laboratories and companies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTravel bans have barely slowed the coronavirus’s spread
Travel restrictions in Wuhan and greater China have only modestly impacted the spread of the virus to other countries, researchers say.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA dog in Hong Kong has a low-level infection of the new coronavirus
There’s currently no evidence that pets can actually get sick from the virus or pass it to people or other animals.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImmune cells in the gut may play a big role in peanut allergies
A study finds loads of allergy-inducing cells in the stomachs and intestines of adults allergic to peanuts, but few in people without the condition.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA more convenient, monthly treatment for HIV cleared a key hurdle
Two phase III clinical trials suggest that a once-a-month injection of antiretroviral drugs treats HIV just as well as daily pill regimes.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyNew fossils and artifacts show Homo erectus crafted a diverse toolkit
Ancient hominid made stone tools demanding a range of skills and planning, a study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistryThirdhand smoke wafting off moviegoers hurts air quality in theaters
Nonsmoking theaters can still get exposed to cigarette-related pollutants carried in on audience members’ bodies and clothing.
-
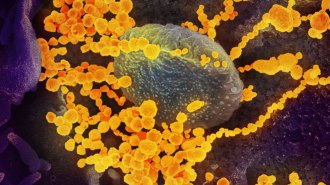 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAs the coronavirus outbreak evolves, we answer some key questions
As the new coronavirus spreads, we are updating this FAQ with the latest on the race to understand the virus and stop the growing global health crisis.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThe ancient hominid species that includes ‘Nutcracker Man’ may have made tools
Newly described hand, arm and shoulder fossils suggest that Paranthropus boisei had powerful arms with hands capable of making simple tools.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine6 key coronavirus numbers you should know
COVID-19 cases and deaths are going up around the world. Here are numbers to help you understand the outbreak.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat the new phase of the coronavirus outbreak in the U.S. means for you
U.S. health experts warn there are probably many undetected COVID-19 cases already here, raising chances the disease will soon be widespread.