Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThere’s no evidence the coronavirus jumped from pangolins to people
Pangolins captured in anti-smuggling activities in southern China were found to harbor viruses related to the new coronavirus.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNeandertals’ extensive seafood menu rivals that of ancient humans
Finds from a coastal cave in Portugal reveal repeated ocean foraging for this European hominid.
By Bruce Bower -
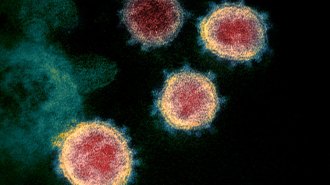 Genetics
GeneticsNo, the coronavirus wasn’t made in a lab. A genetic analysis shows it’s from nature
Scientists took conspiracy theories seriously and analyzed the coronavirus to reveal its natural origins.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNew Guinea’s Neolithic period may have started without outside help
Islanders on New Guinea experienced cultural changes sparked by farming about 1,000 years before Southeast Asians arrived, a study suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYou can help fight the coronavirus. All you need is a computer
With Folding@home, people can donate computing time on their home computers to the search for a chemical Achilles’ heel in the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen will the coronavirus pandemic and social distancing end?
Social distancing may have to continue for months to prevent a resurgence of COVID-19. Wider testing and isolation of cases could ease such measures.
-
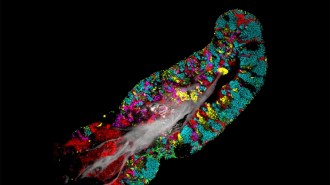 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s where bacteria live on your tongue cells
Scientists labeled bacteria from tongue scrapings with fluorescent probes to glimpse at how the microbes structure their communities.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe number of steps per day, not speed, is linked to mortality rate
Researchers report an association between the total number of steps a person takes each day and the rate of death from any cause.
-
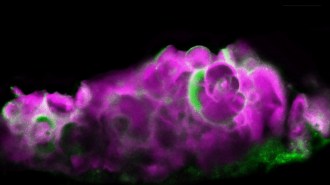 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA tooth-enamel protein is found in eyes with a common form of macular degeneration
Researchers linked a tooth-enamel protein with calcium deposits in eyes suffering ‘dry’ AMD, which could lead to treatments for the vision disorder.
By Alex Fox -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy some heart patients may be especially vulnerable to COVID-19
Researchers don’t yet know if the way the coronavirus enters cells may have something to do with the risks to the heart.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe Nazareth Inscription’s origins may refute ties to Jesus’ resurrection
Chemical analysis shows the tablet’s marble came from a Greek island, challenging the idea the decree concerned early Christianity in the Middle East.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung adults can face severe cases of COVID-19, too
While risk of having a severe case of COVID-19 rises with age, younger adults are also landing in the hospital and ICU, new U.S. statistics show.