Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
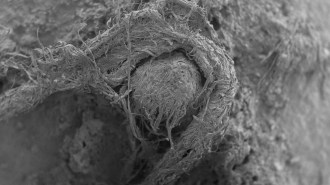
ArchaeologyThis is the oldest known string. It was made by a Neandertal
A cord fragment found clinging to a Neandertal’s stone tool is evidence that our close evolutionary relatives were string makers, too, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
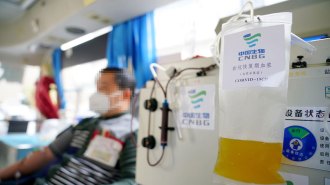
Health & MedicineCan plasma from recovered COVID-19 patients treat the sick?
Researchers are racing to set up clinical trials of antibody-rich convalescent plasma from recovered patients to treat or prevent COVID-19.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJust breathing or talking may be enough to spread COVID-19 after all
Until now, experts have said that the virus spreads only through large droplets released when people cough or sneeze, but it may spread more easily.
-
 Humans
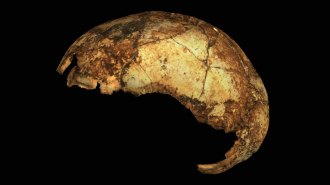
HumansSouthern Africa may have hosted a hominid transition 2 million years ago
Braincases excavated from the Drimolen caves suggest Homo erectus and Paranthropus robustus may have coexisted in southern Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Math
MathHow large a gathering is too large during the coronavirus pandemic?
Mathematical models explain why large gatherings are especially dangerous in an epidemic, and identify how large is too large.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow coronavirus control measures could affect its global death toll
Slowing the virus’ spread will save millions of lives, but differences among countries could vary the pandemic’s toll in different places.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyLucy’s species heralded the rise of long childhoods in hominids
Australopithecus afarensis had prolonged brain growth before the Homo genus appeared, but it still resulted in brains with chimplike neural structure.
By Bruce Bower -
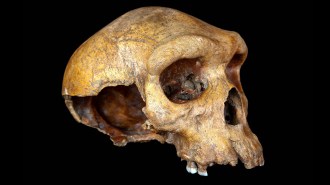 Anthropology
AnthropologyThis 300,000-year-old skull may be from an African ‘ghost’ population
The age of the mysterious Broken Hill fossil suggests it came from a hominid that lived around the same time as both Homo sapiens and H. naledi.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsA cat appears to have caught the coronavirus, but it’s complicated
While a cat in Belgium seems to be the first feline infected with SARS-CoV-2, it’s still unclear how susceptible pets are to the disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSocial distancing comes with psychological fallout
Keeping people apart can help slow the new coronavirus’ spread. But such social distancing may cause or worsen mental health problems.
By Sujata Gupta -
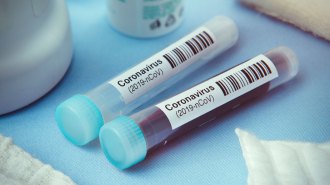 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow antibody tests work and could help fight the coronavirus
Coronavirus antibody tests look for signs in the blood that someone has had an infection and recovered, and could take only a finger prick.
By Dawn Fallik -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFace mask shortages have sparked creative solutions. Will they work?
Homemade masks, reusing masks and even scuba gear are some of the ideas for dealing with health care workers’ lack of supplies during the COVID-19 pandemic.