Rare eastern equine encephalitis has killed 9 people in the U.S. in 2019
31 of the 103 mosquito-borne brain infections in the past decade have occurred in 2019
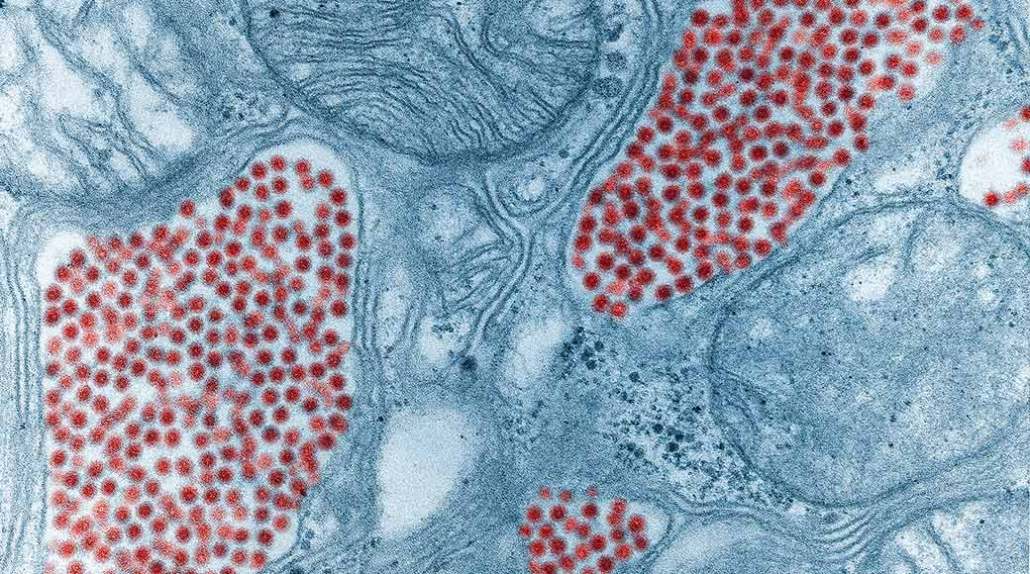
Mosquitoes can spread the virus that causes eastern equine encephalitis. This microscope image shows a mosquito’s salivary glands infected with the EEE virus (red).
Fred Murphy, Sylvia Whitfield/CDC