Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDrugs for high blood pressure don’t appear to make COVID-19 worse
Drugs commonly used to treat hypertension did not lead to more severe cases of the coronavirus infection or higher mortality in hospitalized patients.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 kills more men than women. The immune system may be why
Countries with sex-specific data report more men than women are dying of the coronavirus. Women’s stronger immune response may give them a leg up.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 is hitting some patients with obesity particularly hard
Doctors say some of their sickest COVID-19 patients are young and obese. One study shows they have higher rates of hospital admission and death.
By Dawn Fallik -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore evidence hints that hydroxychloroquine doesn’t help treat COVID-19
A malaria drug showed no benefit over standard care in two preliminary studies examining how well hydroxychloroquine works against the coronavirus.
-
 Humans
HumansHere’s where things stand on COVID-19 tests in the U.S.
Government officials are weighing how to loosen social distancing measures across the United States, but that hinges on widespread COVID-19 testing.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy 6 feet may not be enough social distance to avoid COVID-19
Scientists who study airflow warn that virus-laden drops may travel farther than thought.
-
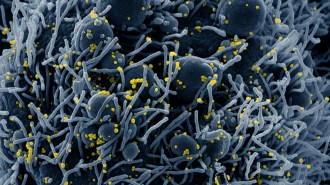 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 may be most contagious one to two days before symptoms appear
The coronavirus probably spreads the most before symptoms appear, making containing viral transmission harder.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy African-Americans may be especially vulnerable to COVID-19
African-Americans are more likely to die from COVID-19 than white Americans, data show. Experts blame long-standing health disparities.
By Sujata Gupta -
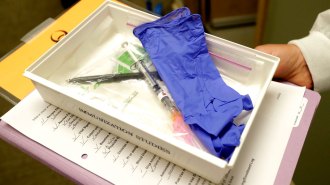 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeet Sophia Upshaw, a volunteer in a coronavirus vaccine trial
In Seattle and Atlanta, scientists have started testing the safety of a potential vaccine to prevent COVID-19.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan fabric masks stem the coronavirus’ spread?
It’s unclear whether homemade masks made from fabric will prevent an infected person from spreading the virus to others, experts say.
-
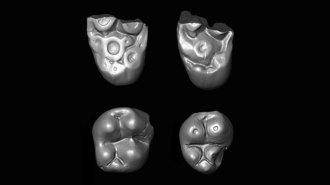 Paleontology
PaleontologyTwo primate lineages crossed the Atlantic millions of years ago
Peruvian primate fossils point to a second ocean crossing by a now-extinct group roughly 35 million to 32 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWarm weather probably won’t slow COVID-19 transmission much
While some evidence has suggested higher temperatures can affect coronavirus transmission, summer’s arrival probably won’t curb the pandemic much.