Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew COVID-19 booster shots have been approved. When should you get one?
The vaccines target the omicron variants currently circulating in the United States.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA newly approved ‘living drug’ could save more cancer patients’ lives
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte, or TIL, therapy is the first T cell treatment for solid tumors. It fights melanoma and maybe other cancers too.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExpanding antibiotic treatment in sub-Saharan Africa could save kids’ lives
Current guidelines limit treatment to infants. Giving antibiotics to at-risk kids under 5, too, has an indirect effect on infant survival, a new trial shows.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Environment
EnvironmentMore than 4 billion people may not have access to clean water
The new estimate, based on data from 135 low- and middle-income countries, is more than double the World Health Organization’s official count.
By Claire Yuan -
 Space
SpaceAstronauts actually get stuck in space all the time
Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams join more than a dozen astronauts who’ve been stranded in space by mechanics, weather or geopolitics since the 1970s.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy mpox is a global health emergency — again
The WHO made the declaration as a potentially more infectious version of the deadly virus has emerged and mpox cases are rapidly rising across Africa.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA hunger protein reverses anorexia symptoms in mice
Boosting levels of protein ACBP spurred the mice to eat and gain weight. It is unclear if any drugs based on the protein might help people with anorexia.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStonehenge’s mysterious Altar Stone had roots in Scotland
New analyses indicate that this weighty piece of the site’s architecture, once thought to come from Wales, was somehow moved at least 750 kilometers.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour medications might make it harder for you to beat the heat
Chronic illnesses and the medications that treat them may make it harder to handle extreme heat. It’s even harder to study how.
-
 Health & Medicine
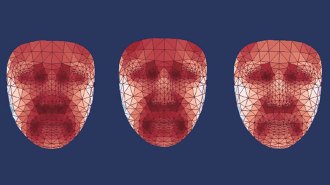
Health & MedicineYour face’s hot spots may reveal how well you are aging
If facial heat maps prove effective at picking up signs of chronic diseases such as diabetes, they could become another health assessment tool.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists blamed migraines on cheese and chocolate
Exactly how migraines develop is still coming into focus, but scientists now know that many factors can trigger attacks.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyWas Egypt’s first pyramid built with hydraulics? The theory may hold water
A controversial analysis contends that ancient engineers designed a water-powered elevator to hoist stones for King Djoser’s pyramid.
By Bruce Bower