Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
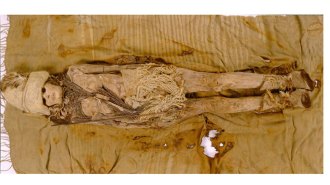
ArchaeologyThe world’s oldest cheese is now revealing some of its secrets
A DNA analysis of the kefir cheese, first found about 20 years ago on 3,600-year-old mummies in China, confirms its age and pinpoints its origins.
-
 Neuroscience
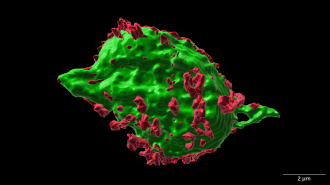
NeuroscienceA study in mice hints at a new way to treat spinal cord injuries
The finding suggests that a drug to ease swelling can speed recovery and stop cell death.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSemaglutide may reduce opioid overdoses, a new study suggests
A study of people with type 2 diabetes and opioid use disorder suggests that the key ingredient in Ozempic and Wegovy shows promise against addiction.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Psychology
PsychologyA brain network linked to attention is larger in people with depression
Brain scans revealed that teenagers with larger attention-driving networks were more likely to develop depression.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBy studying the eyes, a researcher explores how the brain sorts information
Freek van Ede seeks to understand how the brain selects information to plan for the future. He’s finding clues in the tiny movements people make with their eyes.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA cell biologist is investigating the balance of brain flexibility, stability
Andrea Gomez, a Berkeley molecular and cell biologist, applies her wide-ranging curiosity to brains’ mysteries ranging from synapses to psychedelics.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThis researcher studies how misinformation seeps into science and politics
The world is awash in information. Communications researcher Yotam Ophir digs into news articles and survey results to show how beliefs form and spread.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHIV and illicit drugs are a bad mix. This scientist found an unexpected reason why
The neuroscientist considers themself an outsider, which allows them to embrace people who have been marginalized, including people who have HIV.
-
 Climate
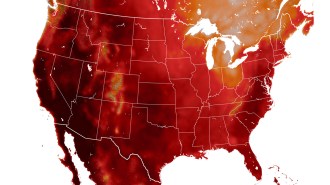
ClimateClimate change could double U.S. temperature-linked deaths by mid-century
Each year, roughly 8,000 deaths in the United States are associated with extreme temperatures. And as temperatures rise, this number could swell.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesSome bacteria in your mouth can divide into as many as 14 cells at once
The filamentous bacterium Corynebacterium matruchotii has a unique reproductive strategy that might allow it to claim territory quickly.
-
 Health & Medicine
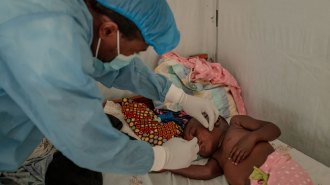
Health & MedicineVaccines for mpox are finally reaching Africa. But questions about the virus remain
With concerns that mpox may now spread more easily and be more severe, researchers warn that failing to curb the outbreak means “nobody is safe.”
-
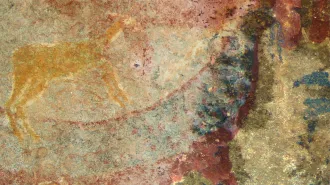 Anthropology
AnthropologyFossils of an extinct animal may have inspired this cave art drawing
Unusual tusks on preserved skulls of dicynodonts influenced the look of a mythical beast painted by Southern Africa’s San people, a researcher suspects.
By Bruce Bower