Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Physics
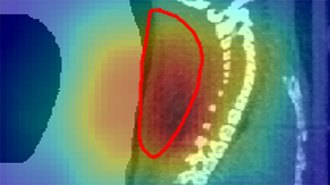
PhysicsRadioactive beams give a real-time view of cancer treatment in mice
This first successful treatment of tumors with radioactive ion beams could one day lead to treating human patients’ tumors with millimeter precision.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA viral gene drive could offer a new approach to fighting herpes
A new gene drive can copy and paste itself into the genomes of herpes simplex viruses in mice. The end goal is a version that disables the virus in humans.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
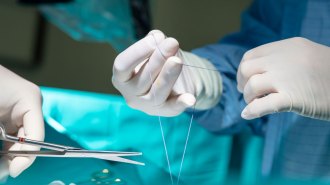
Health & MedicineNew electrical stitches use muscle movement to speed up healing
In rats, the sutures hastened recovery and reduced the risk of infection.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient Scythians had cultural roots in Siberia
A possible sacrificial ritual from around 2,800 years ago suggests mounted herders from Siberia shaped a Eurasian culture thousands of kilometers away.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood pressure may read falsely high if the arm isn’t positioned properly
A clinical trial found blood pressure readings were higher with the arm on the lap or along the side, compared with supported at heart height.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe discovery of microRNA wins the 2024 physiology Nobel Prize
Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun found a new principle of gene regulation essential for all multicellular organisms.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Sophie Hartley -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAn mRNA vaccine protected mice against deadly intestinal C. difficile bacteria
An mRNA vaccine that targets several aspects of C. difficile’s ability to cause severe disease prevented major symptoms and death in mice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrain-controlled bionic limbs are inching closer to reality
Bionics engineers typically view biology as something to be worked around. “Anatomics” engineers the body to be part of the system.
By Simon Makin -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA hurricane’s aftermath may spur up to 11,000 deaths
Hurricanes like Helene may indirectly cause deaths for years. Stress, pollution and a loss of infrastructure could all contribute to tropical cyclone fatalities.
By Meghan Rosen -
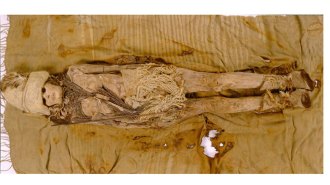 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe world’s oldest cheese is now revealing some of its secrets
A DNA analysis of the kefir cheese, first found about 20 years ago on 3,600-year-old mummies in China, confirms its age and pinpoints its origins.
-
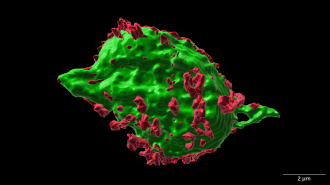 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA study in mice hints at a new way to treat spinal cord injuries
The finding suggests that a drug to ease swelling can speed recovery and stop cell death.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSemaglutide may reduce opioid overdoses, a new study suggests
A study of people with type 2 diabetes and opioid use disorder suggests that the key ingredient in Ozempic and Wegovy shows promise against addiction.
By Meghan Rosen