Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHuman brains found at archaeological sites are surprisingly well-preserved
Analyzing a new archive of 4,400 human brains cited in the archaeological record reveals the organ’s unique chemistry might prevent decay.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyNot all cultures value happiness over other aspects of well-being
Nordic countries topped the 2024 world happiness rankings. But culture dictates how people respond to surveys of happiness, a researcher argues.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLong COVID brain fog may be due to damaged blood vessels in the brain
MRI scans of long COVID patients with brain fog suggest that the blood brain barrier may be leaky.
By Meghan Rosen -
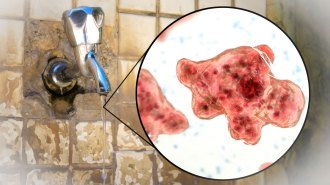 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t use unsterilized tap water to rinse your sinuses. It may carry brain-eating amoebas
Two new studies document rare cases in which people who rinsed sinuses with unsterilized tap got infected with brain-eating amoebas.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe U.S. now has a drug for severe frostbite. How does it work?
Iloprost has been shown to prevent the need to amputate frozen fingers and toes. It’s now approved for use to treat severe frostbite in the U.S.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFour years on, the COVID-19 pandemic has a long tail of grief
Researchers are studying the magnitude and impact that grief from the COVID-19 pandemic has had and will have for years to come.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe blood holds clues to understanding long COVID
A growing cadre of labs are sketching out some of the molecular and cellular characters at play in long COVID, a once-seemingly inscrutable disease.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s why pain might last after persistent urinary tract infections
Experiments in mice reveal that the immune response to a UTI spurs nerve growth in the bladder and lowers the pain threshold.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore than 1 billion people worldwide are now estimated to have obesity
A new analysis suggests that the prevalence of obesity has doubled in women, tripled in men and quadrupled in children and adolescents from 1990 to 2022.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA genetic parasite may explain why humans and other apes lack tails
Around 25 million years ago, a stretch of DNA inserted itself into an ancestral ape’s genome, an event that might have taken our tails away.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSnake venom toxins can be neutralized by a new synthetic antibody
A lab-made protein protected mice from lethal doses of paralyzing toxins found in a variety of snakes, a new study reports.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, computers helped speed up drug discovery
In 1974, a computer program helped researchers search for promising cancer drugs. Today, AI is helping speed up drug discovery.