Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeMeatier meals and more playtime might reduce cats’ toll on wildlife
Outdoor cats kill billions of birds and mammals each year. Simply satisfying their need to hunt or supplementing their diets could lessen that impact.
-
 Life
LifeA reeking, parasitic plant lost its body and much of its genetic blueprint
The Sapria himalayana flower's extreme parasitic lifestyle inside the body of its host has left a bizarre imprint on its genome.
By Jake Buehler -
 Earth
EarthFossil mimics may be more common in ancient rocks than actual fossils
Evidence of early life may be harder to preserve than pseudofossils — structures that form abiotically but resemble living remnants.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA new chameleon species may be the world’s tiniest reptile
The newly described critters, found in the northern forests of Madagascar, may be threatened by deforestation.
-
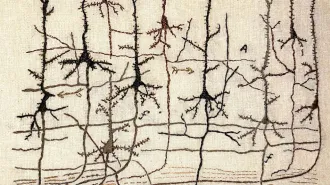 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFamous brain sketches come to life again as embroideries
A needlework project pays tribute to the iconic drawings of Spanish neuroscientist Santiago Ramón y Cajal.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a tiny spider uses silk to lift prey 50 times its own weight
Dropping the right silk can haul mice, lizards and other giants up off the ground.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis ancient sea reptile had a slicing bite like no other
Right up until 66 million years ago, the sea was a teeming evolutionary laboratory with a small, agile, razor-toothed mosasaur patrolling the waters.
By Jake Buehler -
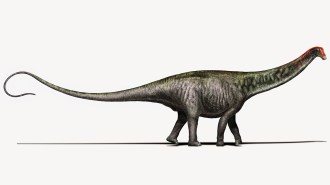 Animals
Animals50 years ago, scientists made the case for a landlubbing Brontosaurus
In 1971, a scientist argued for a landbound Brontosaurus instead of a swampy swimmer. Recent evidence comes from studies of its ancient environment.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsLizard-like tuatara carry two distinct mitochondrial genomes
Having two mitochondrial genetic instruction books, a first for vertebrates, may help explain tuatara’s unique ability to tolerate cold temperatures.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNaked mole-rat colonies speak with unique dialects
Machine learning reveals that these social rodents communicate with distinctive speech patterns that are culturally inherited.
-
 Tech
TechA robot arm toting a Venus flytrap can grab delicate objects
By attaching electrodes to the plant’s leaves, researchers found a way to snap its traps shut on command.
-
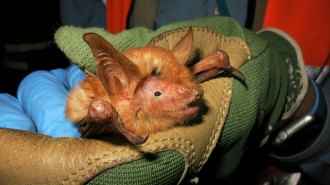 Animals
AnimalsA new orange and black bat species is always ready for Halloween
A new species from the sky islands of Africa’s Nimba Mountains shows bats’ colorful streak.
By Susan Milius